Figure 2.
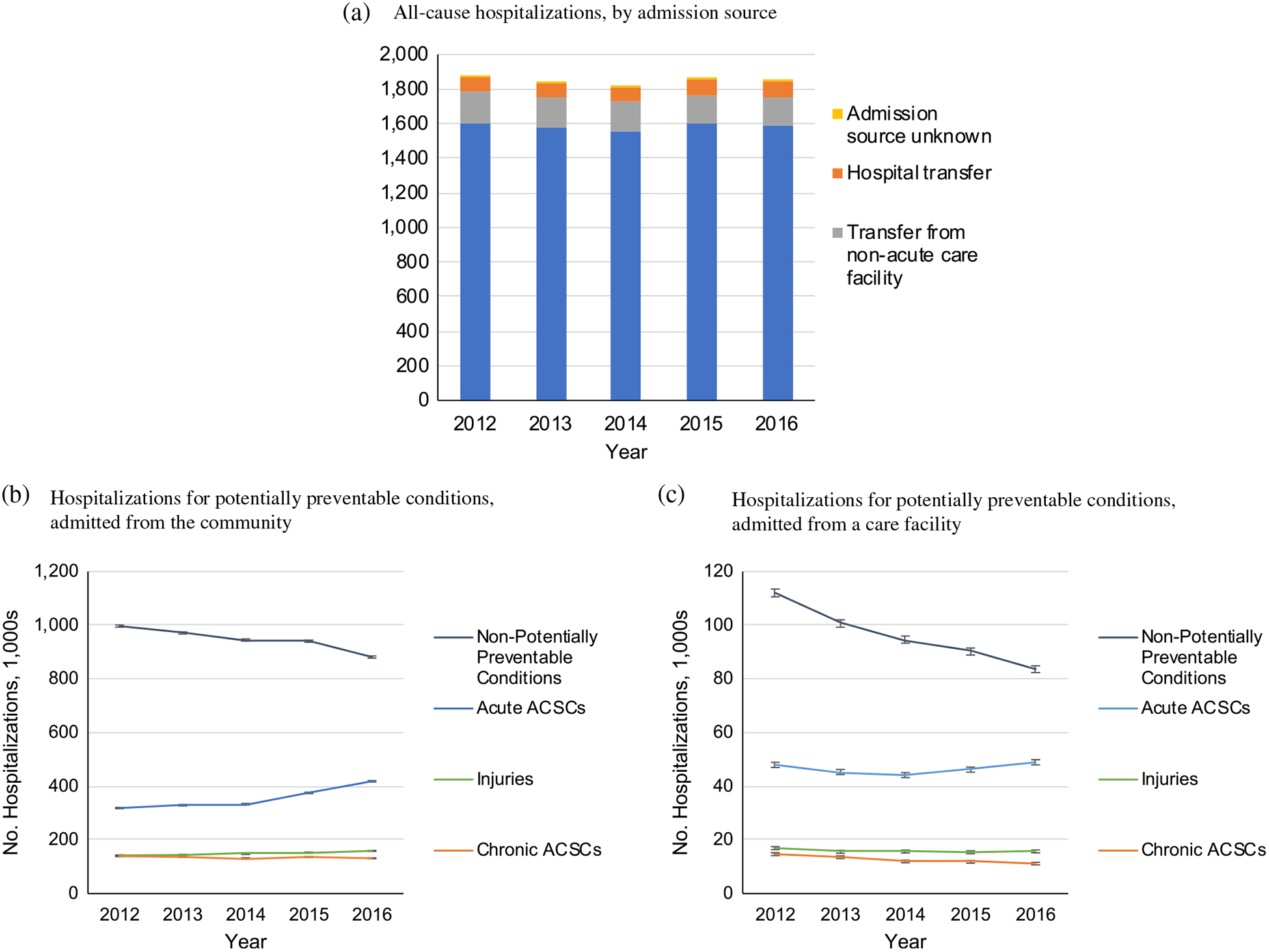
Trends in hospitalizations of older adults with diagnosed dementia, by admission source. (a) All-cause hospitalizations, by admission source. (b) Hospitalizations for potentially preventable conditions, admitted from the community. (c) Hospitalizations for potentially preventable conditions, admitted from a care facility. ACSC, ambulatory care sensitive condition. Note: Preventable conditions include injuries, acute ambulatory care sensitive conditions (ACSCs), and chronic ACSCs. Acute ACSCs include sepsis, urinary tract infection, pneumonia, and dehydration. Chronic ACSCs include congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, and hypertension. Injuries include fractures, other traumatic injuries, medical and surgical complications, poisonings, and other injuries. Non-acute care facilities include skilled nursing, other non-acute care facility, and home health care. All data are weighted to be nationally representative. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. Panel (A): All trends statistically significant (P < .001) except for admissions from source unknown (P = .80). Panel (B): All trends statistically significant (P < .001) except for injuries (P = .85). Panel (C): All trends statistically significant (P < .001).
