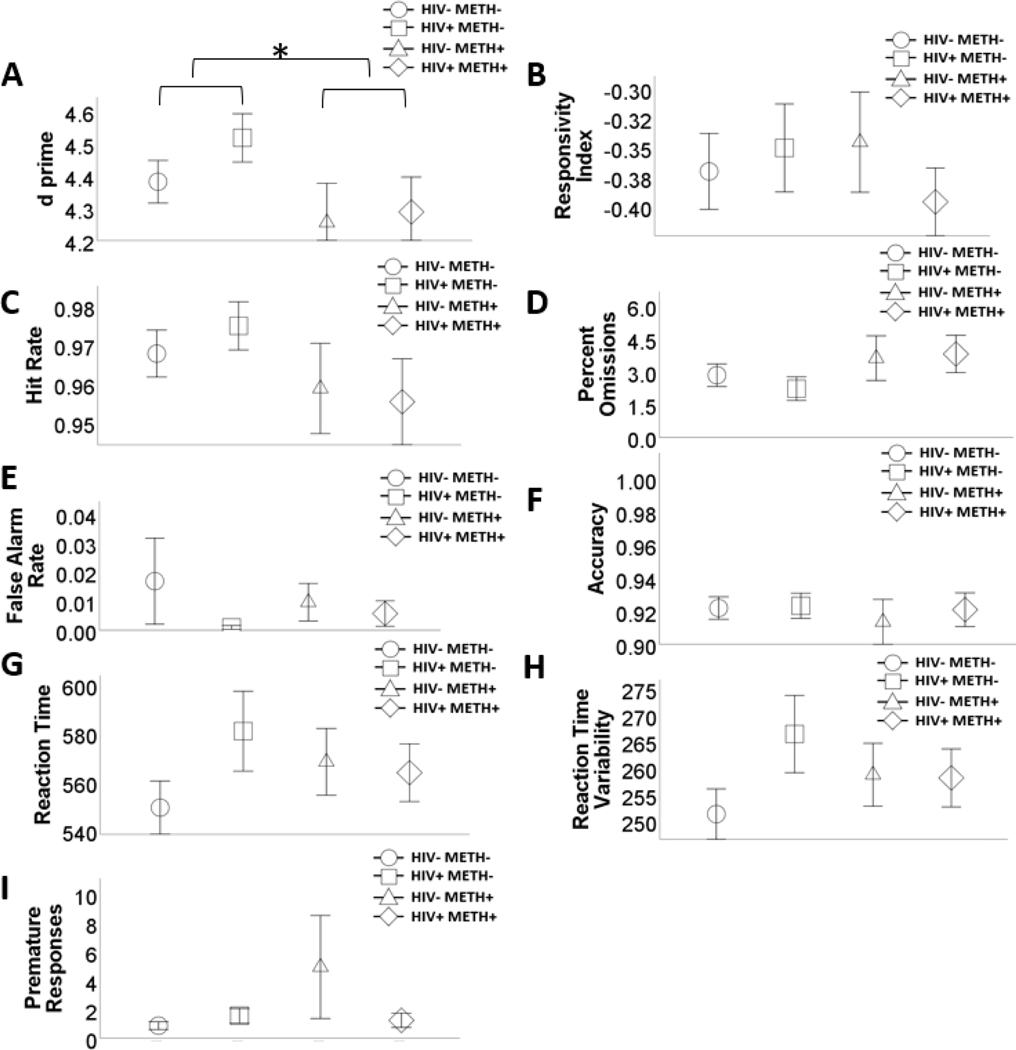
Figure 1.
Effects of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and history of methamphetamine dependence (METH) on 5C-CPT performance.
N = 203. METH+ had lower d prime, relative to METH- people (A). There were no main or interactive effects of HIV and METH on any of the other outcome variables (B – I). Data are presented as means, with error bars representing standard error of the mean. Significant differences are denoted with an asterisk. Corresponding regression estimates, standard errors, and bootstrapped 95% confidence intervals presented in Table 2.