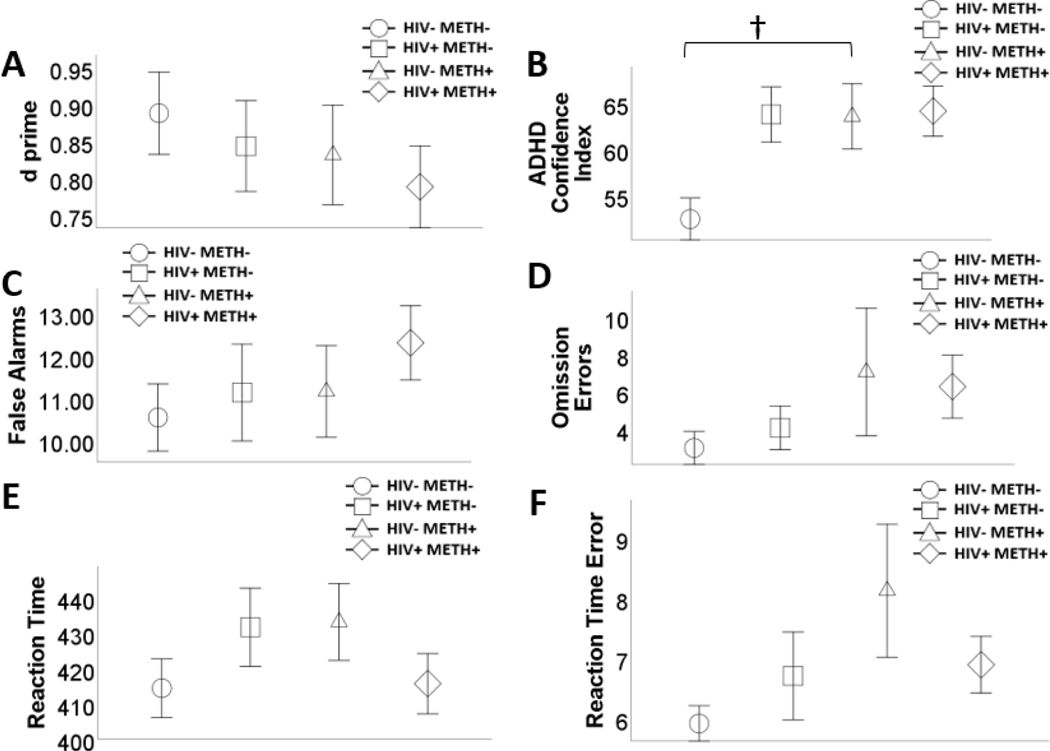
Figure 3.
Effects of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and history of methamphetamine dependence (METH) on Conners’ CPT performance. N = 203. There was a significant HIV x METH interaction on attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) confidence index (prior to Bonferroni correction), such that among HIV-people, METH+ was associated with greater ADHD confidence index. METH+ was not associated with ADHD confidence index among people with HIV (A). There were no main or interactive effects of HIV and METH on any of the other outcome variables (A – F). Data are presented as means, with error bars representing standard error of the mean. Significant difference prior to Bonferroni correction (i.e., p<.05) is denoted with a †. Corresponding regression estimates, standard errors, and bootstrapped 95% confidence intervals presented in Table 5.