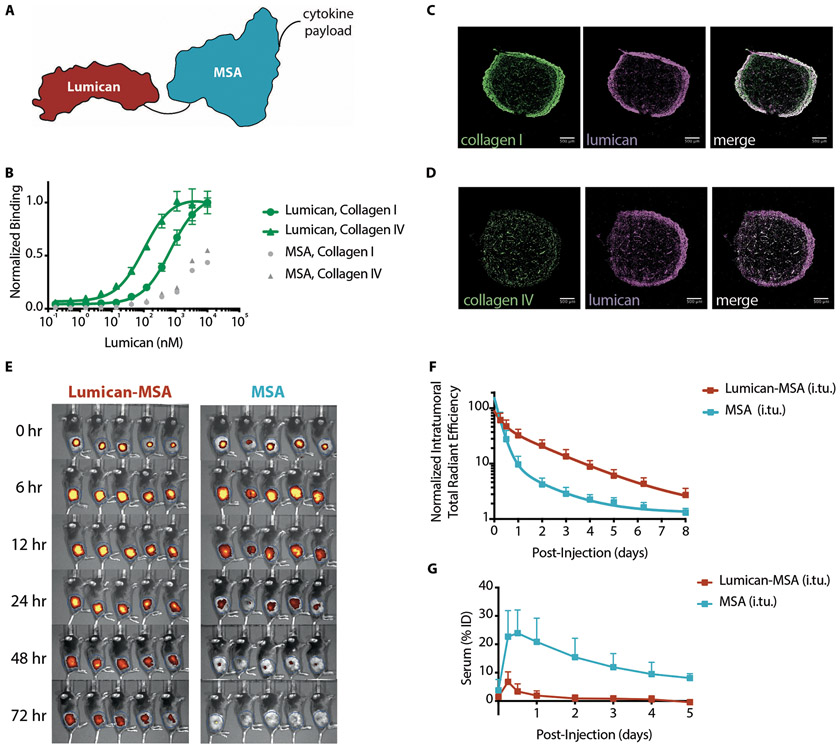
Fig. 1. Lumican binds collagen and demonstrates prolonged retention and systemic isolation after intratumoral injection.
(A) Schematic of a sample fusion protein used to anchor cytokines to intratumoral collagen when locally injected. Black lines represent glycine-serine linkers between collagen-binding protein lumican (red), mouse serum albumin (MSA, blue), and the cytokine. (B) Lumican binding to collagen types I and IV was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (n = 4, mean +/− S.D.). MSA serves as a nonspecific protein control. (C and D) Representative immunofluorescence images of B16F10 tumors excised, fixed, and frozen four days after intratumoral injection of fluorescently labeled Lumican (middle, purple). Sections were stained for either collagen (C) type I (left, green) or (D) type IV (left, green). White pixels in the merged composites (right) represent areas of colocalization between lumican and the respective collagen stain. Scale bars are 500 μm. (E) Images and (F) quantification of intratumoral retention and (G) serum fluorescence as a percentage of the injected dose (ID) of labeled Lumican-MSA and MSA after injection into B16F10-TRP2KO tumors (n = 5, mean + S.D.).