Figure 3.
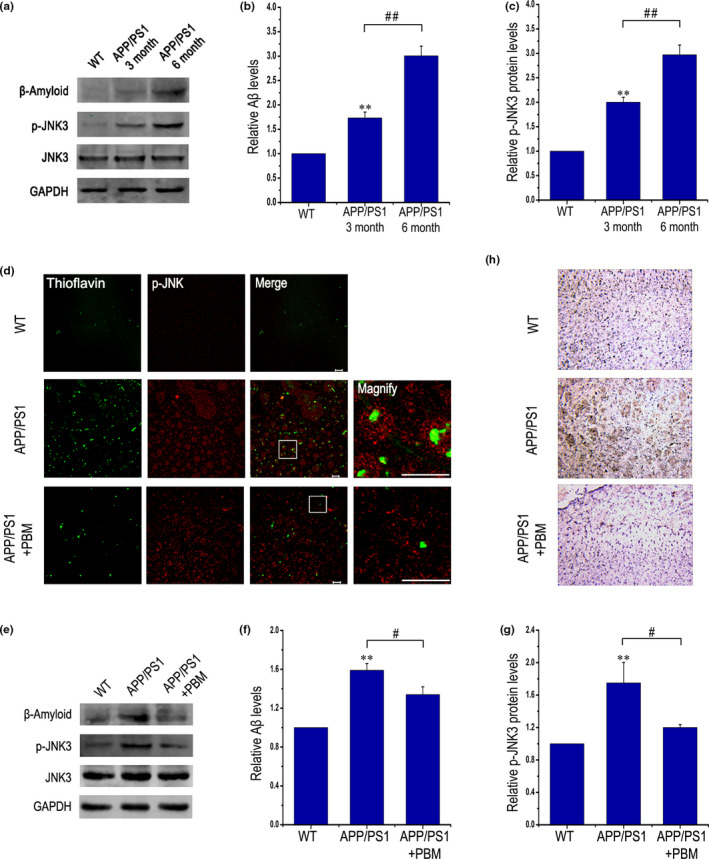
PBM inhibits JNK3 phosphorylation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. (a–c) Western blot analysis of cortex lysates from WT mice and APP/PS1 transgenic mice at three and 6 months of age (n = 3 for each group, at least three individual experiments, mean ± SEM, one‐way ANOVA, **p < 0.01 vs. age‐matched WT group, ##p < 0.01 vs. indicated group). (d) Representative immunofluorescent images of p‐JNK in the cortex. Also shown are images of thioflavin T staining from the frontal cortex. Scale bar, 20 μm. (e–g) Aβ and p‐JNK expression were detected by Western blot in cortex lysates from APP/PS1 transgenic mice with or without PBM (6 J/cm2) and age‐matched WT mice (n = 5, at least three individual experiments, mean ± SEM, two‐way ANOVA, *p < 0.05 vs. control group, **p < 0.01 vs. control group, #p < 0.05 vs. indicated group, ##p < 0.01 vs. indicated group). (h) Immunohistochemical test performed to detect p‐JNK in sections of brain from APP/PS1 transgenic mice with or without PBM (6 J/cm2) and age‐matched WT mice; original magnification of 20 times. See Figure S3 for inhibition of PBM on JNK3 phosphorylation and APP Thr668 phosphorylation in an AD transgenic mouse model. And also please refer to Figure S4 to view that the potential disease‐modifying therapeutic mechanism of PBM on memory impairment and Aβ load, which is likely achieved by regulate JNK3, in APP/PS1 mice
