FIGURE 5.
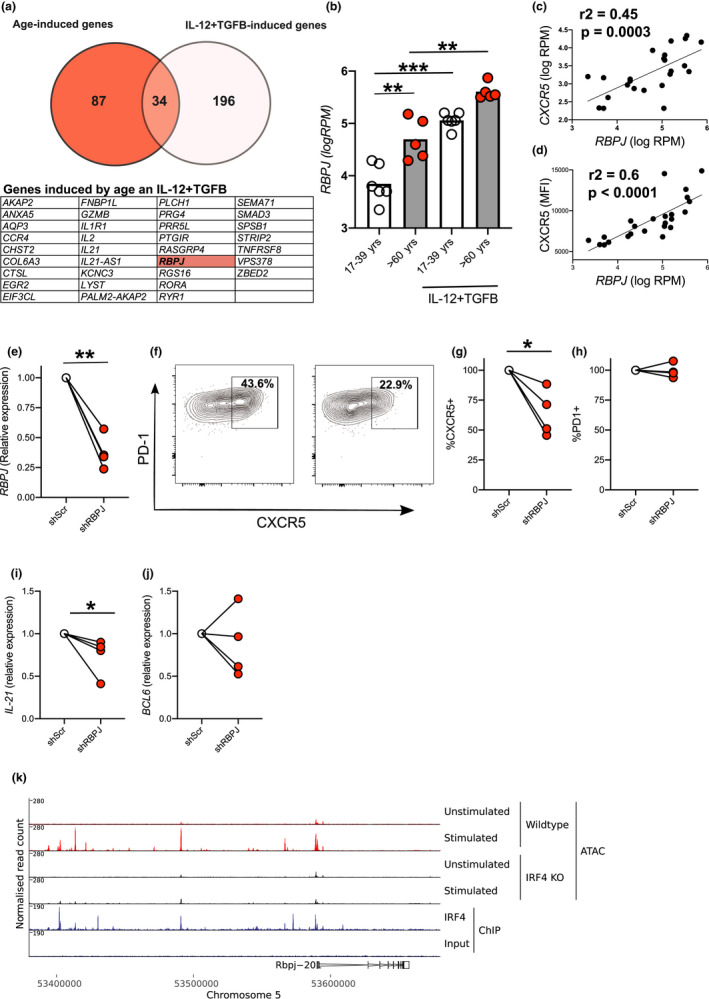
Role for transcription factor RBPJ in age‐associated CXCR5 expression in human CD4+ T cells. Venn diagram summarising data from RNA‐Seq analysis where age‐induced genes are shown in red and cytokine‐induced genes in white with the 34 genes present in both samples listed in the table (a). Bar graph showing individual values of normalised reads for RBPJ in RNA‐Seq libraries in the different cell culture conditions indicated (b). Correlations between levels of RBPJ with expression of CXCR5 as determined by both RNA‐Seq (c) and flow cytometry (d) on the same samples 72 hr postactivation. Graphs showing inhibition of RBPJ expression by shRNA as determined by RT‐PCR (e). Representative flow cytometry plots showing effect of shRBPJ and control (shScr) on pre‐Tfh cell differentiation at 72 hr postactivation (f). Graphs showing CXCR5 (g), PD‐1 (h) protein expression, IL21 (i) and BCL6 (j) relative to inhibition by control lentivirus (shScr) for CD4+ cells from individual older donors. ATAC‐Seq of naïve and activated (72 hr) Wt and Irf4 −/− mouse CD4+ T cells at Rbpj locus. IRF4 ChIP‐Seq tracks showing site of IRF4 binding within the Rbpj locus of naïve murine CD4+ T cells (k). Each symbol is representative of individual values from independent donors. Statistics calculated using Mann–Whitney U test, paired test *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005
