FIGURE 6.
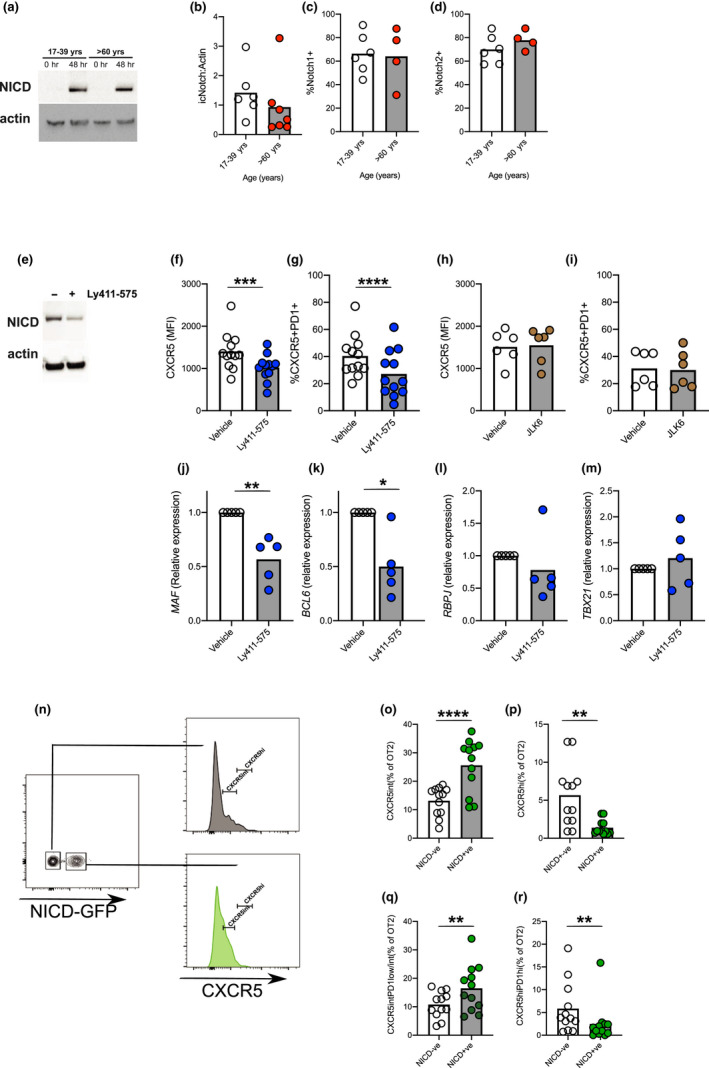
Increased RBPJ expression enables Notch to drive CXCR5 expression. Western blot (a) and quantification (b) of cleaved form of NICD after 48 hr of CD3/CD28 stimulation of human naïve CD4+ T cells from younger and older people. Levels of NICD relative to α‐actin and are shown for younger and older donors (b). Surface expression of Notch 1 (c) and Notch 2 (d) as determined by flow cytometry following 48 hr CD3/CD28 activation of human naïve CD4+ T cells from younger (clear circles) and older (red circles) donors. Western blot of NICD levels after treatment of CD3/CD28‐activated human naïve CD4+ T cells in the presence of a partially inhibiting dose of Ly411‐575 (e). Effect of gamma‐secretase inhibitors Ly411‐575 (50 nM) and JLK6 (5uM; Notch inactive) on CXCR5 expression and pre‐Tfh cell differentiation of human naïve T cells from donors >60 years of age following stimulation via CD3/CD28 (f–i). The expression of MAF (j), BCL6 (k), RBPJ (l), TBX21 (m), mRNA as determined by RT‐PCR 72 hr postactivation in the presence of Ly411‐575. Representative flow cytometry plots of active Notch (NICD‐GFP) in transferred murine OT‐II T cells taken from draining lymph nodes 6 days postimmunisation, and CXCR5 expression on GFP−CD4+ cells (top, grey) and GFP+CD4+ cells (lower, green; n). Graphs showing proportion of CXCR5int (o) and CXCR5hi (p), Pre‐Tfh (q) and GC‐Tfh (r) cells in either GFP+NICD+ or GFP−NICD− murine OT‐II T cells. Each symbol is representative of individual values from independent mice or donors. Statistics calculated using Mann–Whitney U test *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005, ****p < 0.0001
