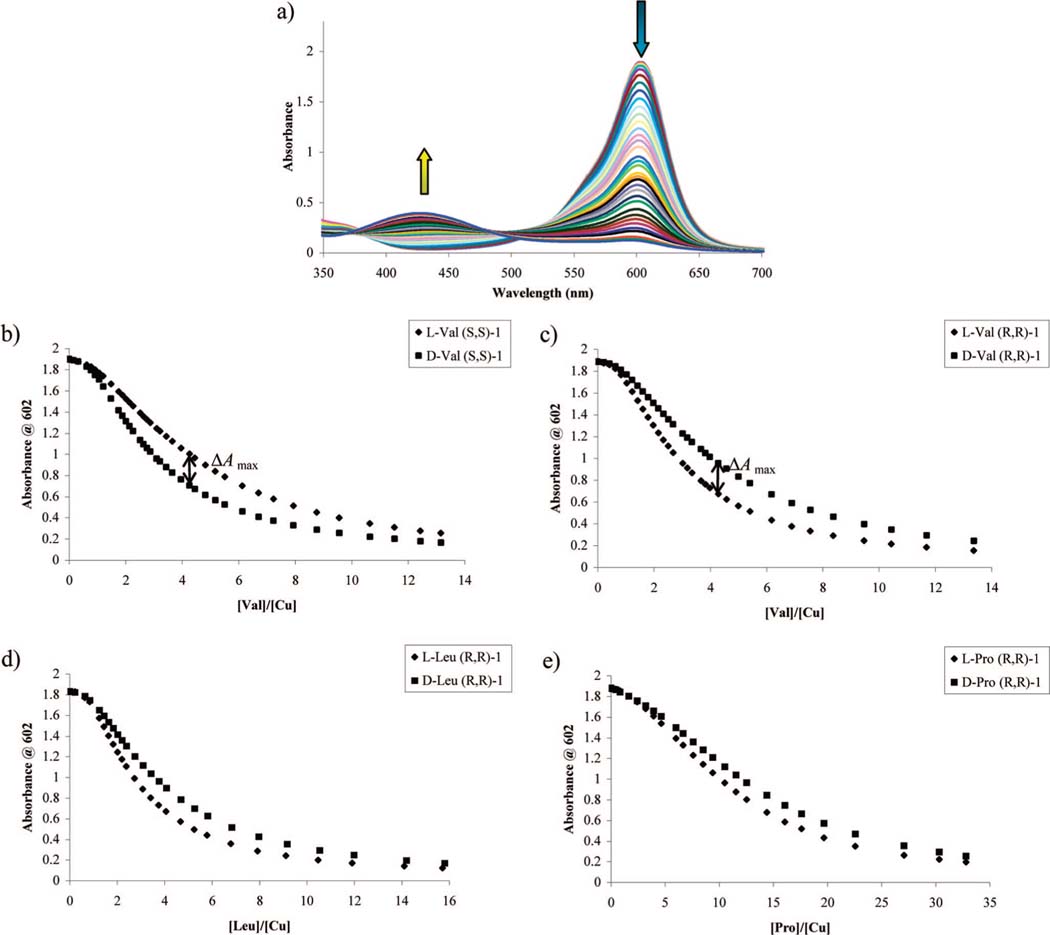
Figure 4.
(a) Hypsochromic absorbance shift upon the addition of l-valine (5.01 mM) into a solution of CAS (10 μM), Cu(OTf)2 (200 μM), and (R,R)-1 (2.5 mM) in 1:1 MeOH:H2O, 50 mM HEPES buffered to pH 7.5. (b) Displacement isotherms at 602 nm upon the addition of l- or d-valine (5.01 mM) into a solution containing CAS (10 μM), Cu(OTf)2 (200 μM), and (S,S)-1 (2.5 mM) in 1:1 MeOH:H2O, 50 mM HEPES buffered to pH 7.5. (c-e) Displacement isotherms at 602 nm obtained for a solution containing CAS (10 μM), Cu(OTf)2 (200 μM), and (R,R)-1 (2.5 mM) in 1:1 MeOH:H2O, 50 mM HEPES buffered to pH 7.5, upon the addition of (c) l- or d-valine (5.01 mM), (d) l- or d-leucine (5.11 mM), or (e) l- or d-proline (9.96 mM). ΔAmax is defined as the largest difference in absorbance observed in separate titrations of a [CuII((R,R)-1)(CAS)]2– solution at the same concentration of d- and l-amino acid.