FIGURE 7.
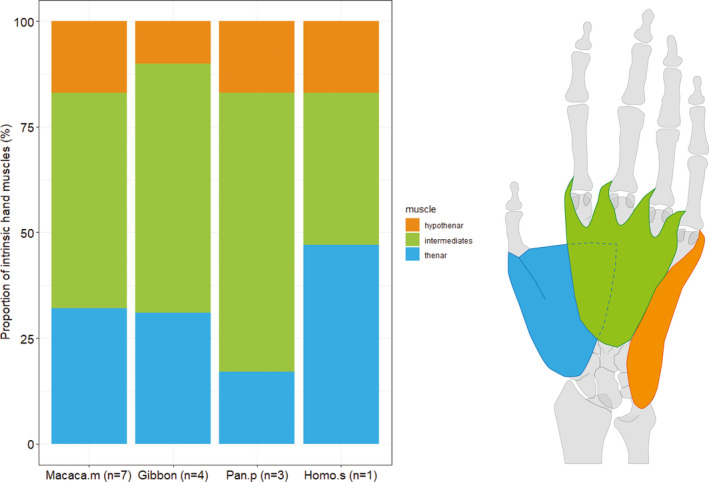
The composition of the intrinsic hand muscles is very similar in gibbons and macaques, with a dominant development (%PCSA) of the intermediate hand muscles (~59% and ~51% respectively), the thenar PCSA taking up approximately 30% of the total intrinsic PCSA and the hypothenar muscle PCSA amounting to only 10% and 18%. In bonobos, the intermediate hand muscles take up a larger proportion of the total intrinsic PCSA (~66%), while in humans, the thenar PCSA is relatively more prominent (~47%). The proportion of the intrinsic hand muscle PCSA relative to total forearm muscle PCSA is 14.7% in macaques, 14.5% in gibbons and humans and 18.4% in bonobos (p > .05)
