FIGURE 1.
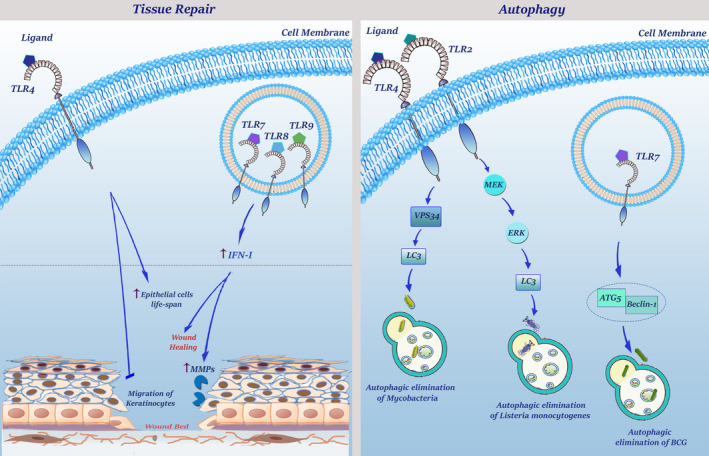
Non‐canonical functions of TLRs. TLRs play an important role in wound healing and tissue repair. TLR4 signalling inhibits migration of keratinocytes and its expression on epithelial cells results in an increased survival. Stimulation of TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 have also anti‐apoptotic effects on fibroblasts through induction of type I interferons. In addition, TLRs can regulate wound healing response by attenuating fibroblast migration and increasing MMPs. Control and regulation of autophagy are another physiological function of TLRs. TLR4 signalling leads to LC3 aggregation via the TRIF signalling pathway which engages VPS34. Autophagic elimination of BCG can be triggered by TLR7 which uses the MyD88 signalling pathway to recruit Beclin‐1 and ATG5. TLR2 activation cascade also results in ERK phosphorylation, which in turn leads to the formation of the LC3 complex that is needed for listeria monocytogenes autophagic elimination
