Figure 3. Cytoplasmic CycA2 triggers polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) activation.
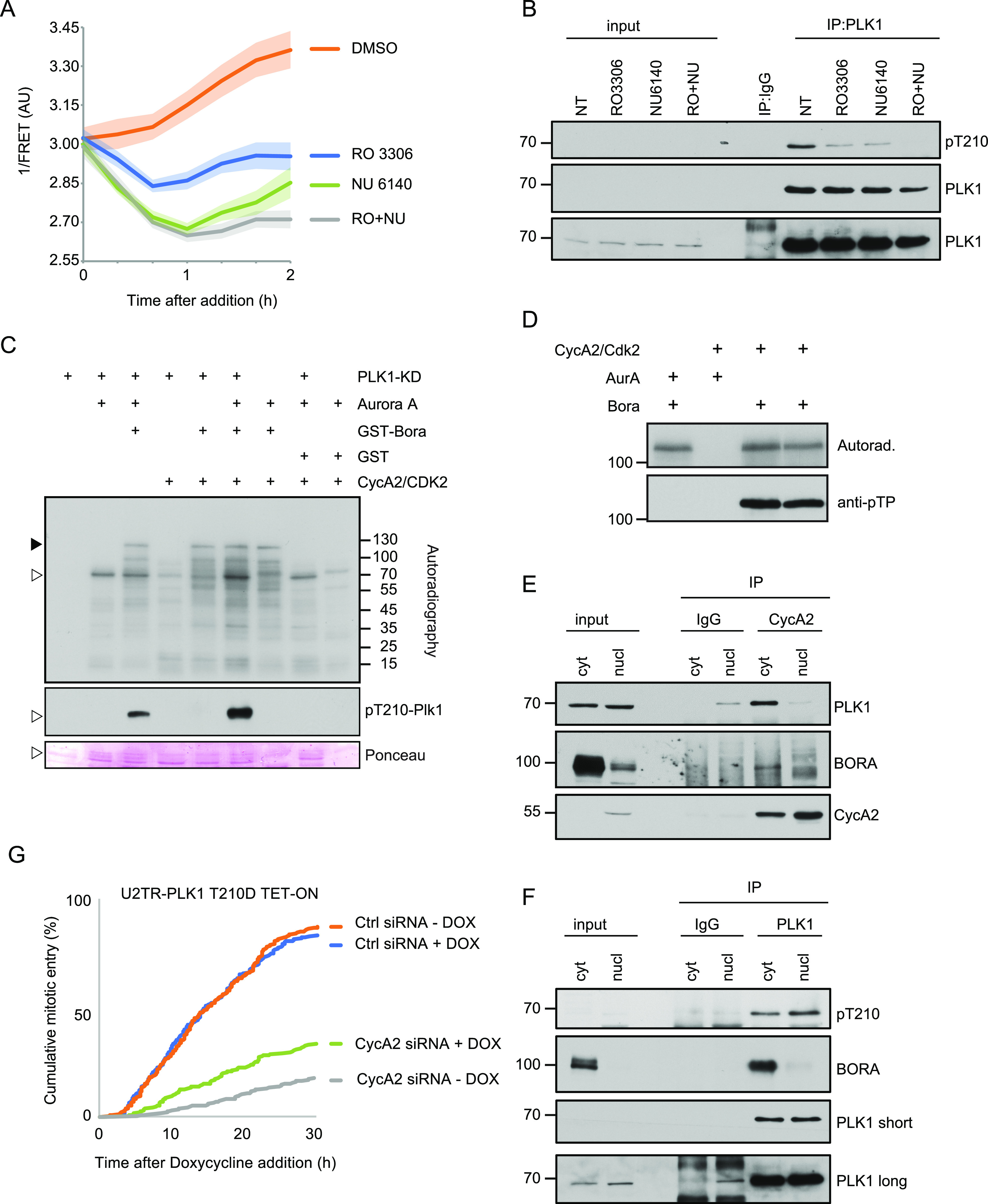
(A) Inhibition of cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) activity in U2OS cells expressing PLK1 FRET reporter. Cells with intermediate PLK1 FRET signal, indicative of G2 phase, were followed after addition of indicated inhibitors. Graph shows average and s.e.m of at least 10 cells per condition. (B) Inhibition of CDK activity in RPE cells synchronised in G2 decreases the level of PLK1 phosphorylation at T210. PLK1 blot is shown twice using a high and a low exposure. (C) Phosphorylation of Bora by CycA2-CDK2 promotes modification of PLK1 at T210 mediated by Aurora-A. Empty arrowhead indicates position of the kinase dead PLK1, full arrowhead indicates position of Bora. (D) CycA2-CDK2 can phosphorylate Bora on SP/TP sites. (E, F) Cytosolic and nuclear extracts from RPE cells synchronised in G2 phase were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-CycA2 (E) or anti-PLK1 (F) antibodies and bound proteins were probed with indicated antibodies. For (E), data using additional antibodies can be found in Fig 4C. (G) Expression of PLK1 T210D can partially rescue CycA2 siRNA-mediated cell cycle arrest. U2TR cells with inducible expression of PLK1 T210D were transfected with CycA2 siRNA. 20 h later, Doxycycline was added and cells were followed using phase contrast time-lapse microscopy. 300 cells per condition were followed manually over time. All experiments were repeated at least three times.
