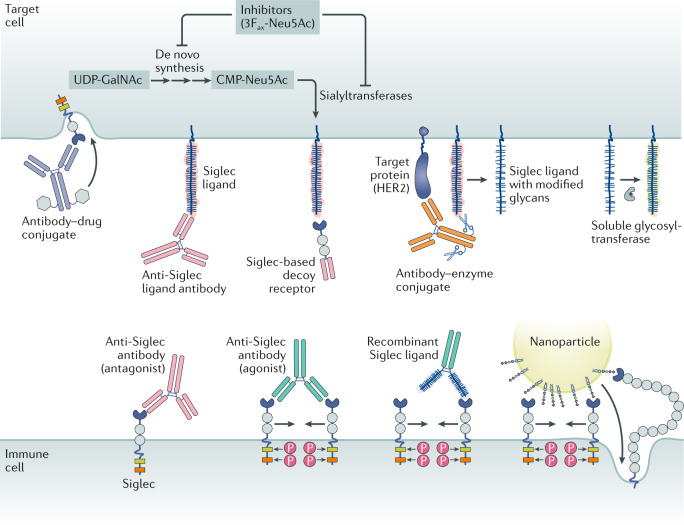
Fig. 5. Modalities for Siglec-targeted therapies.
Antibody–drug conjugates target the Siglecs (CD22 and CD33) that are expressed by cancers, including acute myeloid leukaemia and B cell lymphomas. Anti-Siglec antibodies can either agonize or antagonize Siglec activity. Siglec-blocking antibodies can function as antagonists by preventing ligand binding, but many serve as mild agonists by promoting dimerization. Siglec agonist antibodies can dampen immune cell activity and promote apoptosis. Siglec ligand-blocking antibodies antagonize Siglec function via competitive binding to the Siglec ligand. Recombinant Siglec ligands, shown here as a recombinant glycoprotein fused to an antibody Fc domain, could theoretically act as either receptor agonists or antagonists, likely depending on their ability to cluster Siglecs. Siglec-based decoy receptors comprising a soluble Siglec protein bind to and block the set of ligands for any given Siglec. Therefore, they may antagonize Siglec activity when ligand identities are unclear or diverse. Antibody–enzyme conjugates comprise antibodies directed to target cell-specific antigens conjugated to a glycocalyx editing enzyme such as a sialidase. In the case of an antibody–sialidase conjugate, removal of sialic acid destroys Siglec ligands, thereby antagonizing immune cell Siglecs. Glycosyltransferases in circulation or administered therapeutically may use nucleotide sugars released from platelets to alter the glycocalyx by creating or destroying Siglec binding sites. Nanoparticles such as liposomes bearing Siglec ligands may agonize Siglecs via aggregation or serve as a means for targeted payload delivery. Finally, small-molecule inhibitors, such as the fluorinated sialic acid analogue 3Fax-Neu5Ac154, of de novo sialic acid synthesis, or the sialyltransferases, the enzymes responsible for linking sialic acid to nascent glycoproteins and glycolipids, may reduce the sialic acid content of the glycocalyx and destroy Siglec ligands. CMP-Neu5Ac, cytidine monophosphate-N-acetyl-neuraminic acid; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (also known as ERBB2); P, phosphate; UDP-GalNAc, uridine diphosphate-N-acetyl-galactosamine.