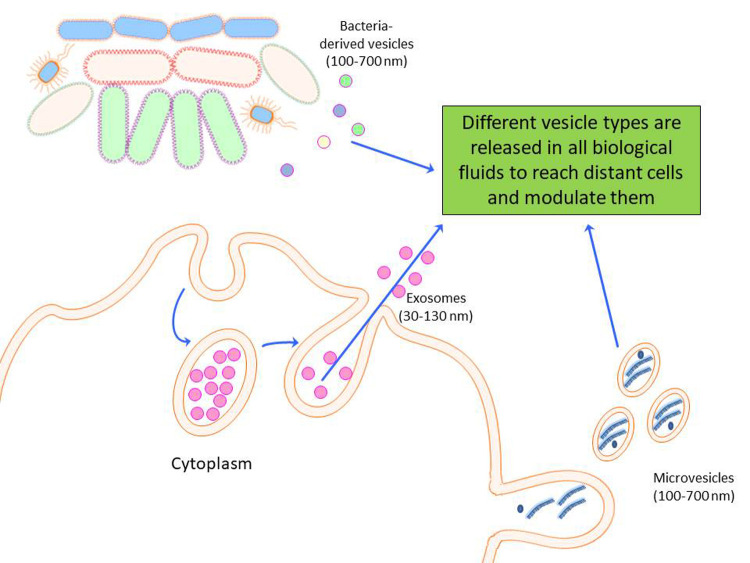
Figure 5.
Extracellular vesicles are a heterogeneous group of membrane vesicles, including microvesicles and exosomes, which are released from cells under both physiological and pathological conditions. Extracellular vesicles play a central role in cell-to-cell communication, as they are able to transfer between cells biological active molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids. Extracellular vesicles contain microRNAs, being able to modulate cell expression “at a distance”, and they have been detected in most body fluids, including blood, urine, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, amniotic fluid, seminal plasma, and breast milk