Fig. 3.
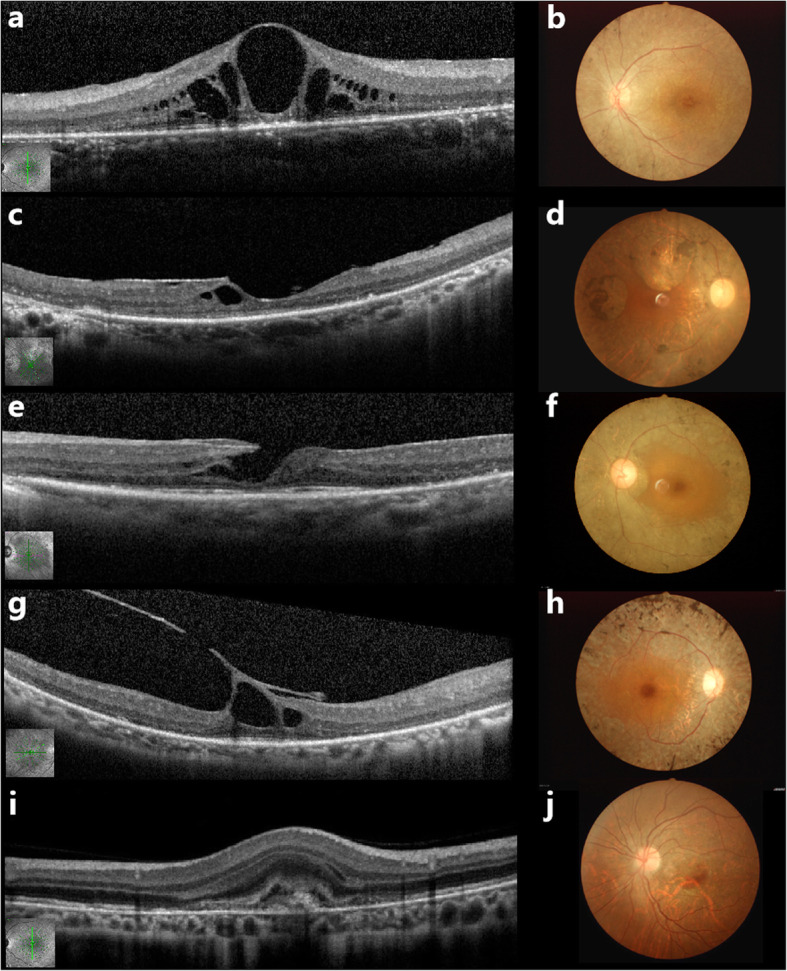
Representative optical coherence tomography (OCT) and corresponding fundus photography of RP patients with macular abnormalities. a An OCT image with cystic-appearing spaces in the left eye. b Fundus photograph of the left eye in picture a, showing bone spicule pigmentation in the mid-periphery and vessels attenuation. c OCT scan showed a homogenous layer of moderately reflective material, present on the inner retinal layer. d Fundus photography of the right eye in picture c, showed marked bone spicule pigmentation in the mid-periphery, waxy pallor of the optic disc and attenuated vessels. e OCT scan with lamellar macular hole. f: Fundus photography of the picture e, revealed bone spicule pigmentation in the mid-periphery and vessels attenuation. g OCT scan showed vitreomacular traction. h Fundus photography of the right eye in picture g, showed marked bone spicule pigmentation in the mid-periphery, waxy pallor of the optic disc and attenuated vessels. i OCT image showed disruption of the Bruch membrane/retinal pigment epithelium complex, accompanied by a hyper-reflective lesion connected with the subretinal pigment epithelium. j Fundus photography of the left eye in picture i, showed hemorrhage located in the inferior-temporal macular area
