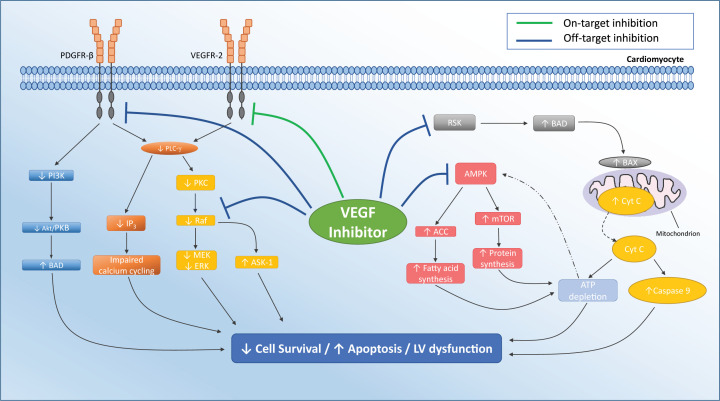
Figure 4. Pathways by which VEGF inhibitors cause direct myocardial toxicity.
Inhibition of ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) may lead to activation of the pro-apoptotic factor BAD. This leads to BAX activation and Cyt C release from mitochondria. This, in turn, leads to ATP depletion and activation of caspase 9 and can lead to apoptosis. Normally, ATP depletion would lead to activation of AMP kinase (AMPK); however, VEGFI inhibition of AMPK prevents this action, leading to increased activation of ACC and mTOR activity and further ATP depletion by fatty acid and protein synthesis. Inhibition of PDGFR-β leads to decreased PI3K, which may lead to up-regulation of pro-apoptotic BAD pathway. Direct inhibition of Raf-1 may down-regulate the MEK-ERK pathway, reducing cell survival. Additionally, Raf-1 inhibition may prevent the inhibition of pro-apoptotic kinases such as ASK-1. On-target inhibition of VEGFR-2 may down-regulate PLC-γ leading to reduced IP3 and impaired calcium cycling, which may reduce myocardial contractility. Abbreviations: ACC, acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase; ASK-1, apoptosis-signal-regulating kinase-1; BAD, BCL2-antagonist of cell death; BAX, BCL2-associated X protein; Cyt C, cytochrome c; IP3, inositol-trisphosphate-3 kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K, phosphatidyl inositol-3 kinase; PLC- γ, phospholipase C; PKC, Protein kinase C; PDGFR-β, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; Raf-1, rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma-1.