Fig. 5.
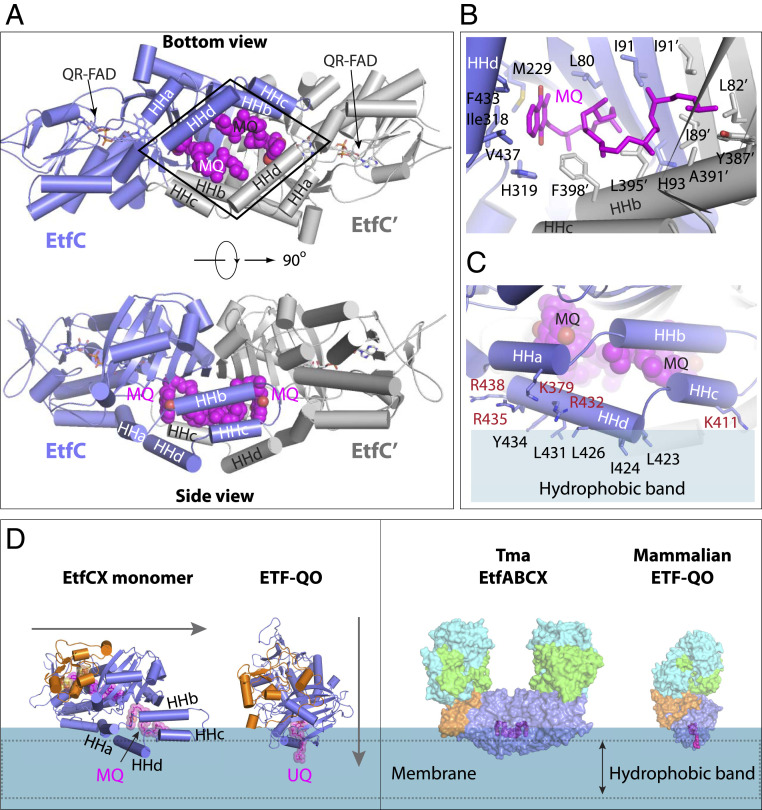
EtfC dimer interface plays a dual function in MQ binding and membrane embedding. (A) A bottom view (Top; from membrane) and side view (Bottom) of the EtfC dimer showing two MQ molecules lying flat inside the rhombic pocket formed by the C-terminal α-helices HHa to HHd. (B) Each MQ is surrounded by 15 highly hydrophobic residues. (C) A side view of one EtfC showing five positively charged residues above five hydrophobic residues of the C-terminal α-helices HHa, HHc, and HHd. Such surface property is compatible with membrane embedding. (D, Left) The presence of the four C-terminal α-helices HHa to HHd enables EtfC to insert horizontally into the membrane, as compared with the vertical insertion of the ETF-QO. (D, Right) The approximate membrane-embedding region of the Tma EtfABCX superdimer complex compared with the mammalian ETF QO.