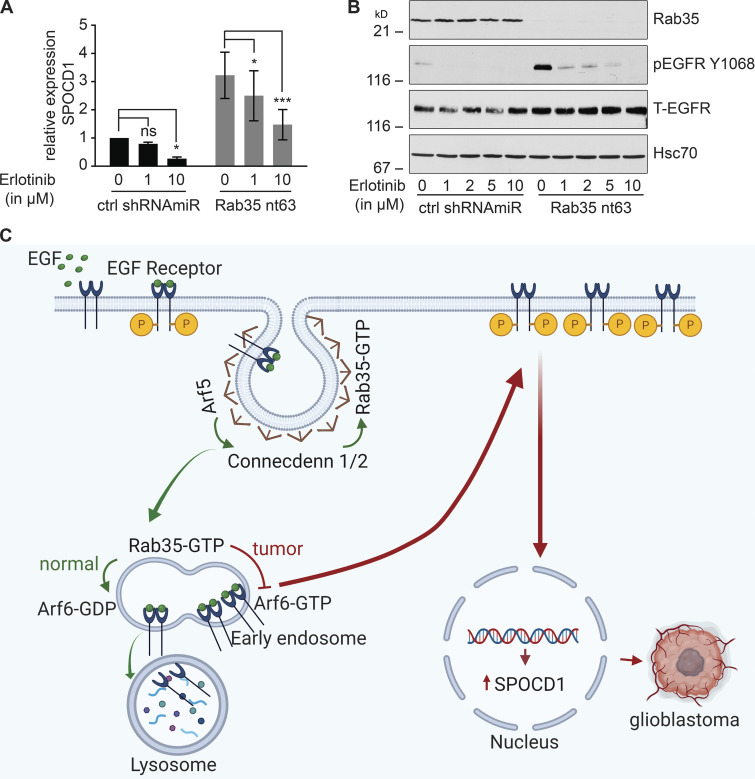
Figure 9.
SPOCD1 is up-regulated downstream of activated EGFR. (A) U87 glioblastoma cells were transduced with a control (ctrl) shRNAmiR or a shRNAmiR targeting Rab35. After 3 d in culture, cells were treated with various concentrations of erlotinib, a specific EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, for 24 h. RNA was prepared from the cells and analyzed for the levels of SPOCD1 by quantitative PCR. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis employed a two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test; n = 5; ***, P < 0.001; *, P < 0.05; ns, not significant. (B) Cells transduced and treated as in A were processed for immunoblot with antibodies recognizing the indicated proteins. The migration of molecular mass markers (in kD) is indicated. (C) Connecdenn 1/2 (DENND1A/B) on clathrin-coated pits interact, through their DENN domains, with Arf5, which stimulates connecdenn GEF activity toward Rab35. The activated Rab35 on endosomes inhibits Arf6 by binding to an Arf6 GAP. This inhibits Arf6, preventing EGFR recycling and driving the receptor toward lysosomes. Disruption of Arf5/Rab35, via knockdown or in tumors, leads to loss of inhibition of Arf6, which enhances EGFR recycling. The high levels of EGFR lead to autoactivation and signaling to up-regulate the expression of SPOCD1 that triggers glioblastoma growth. P indicates receptor phosphorylation. This illustration was created using BioRender.