Figure 1: Diversity of the human RTK ligands.
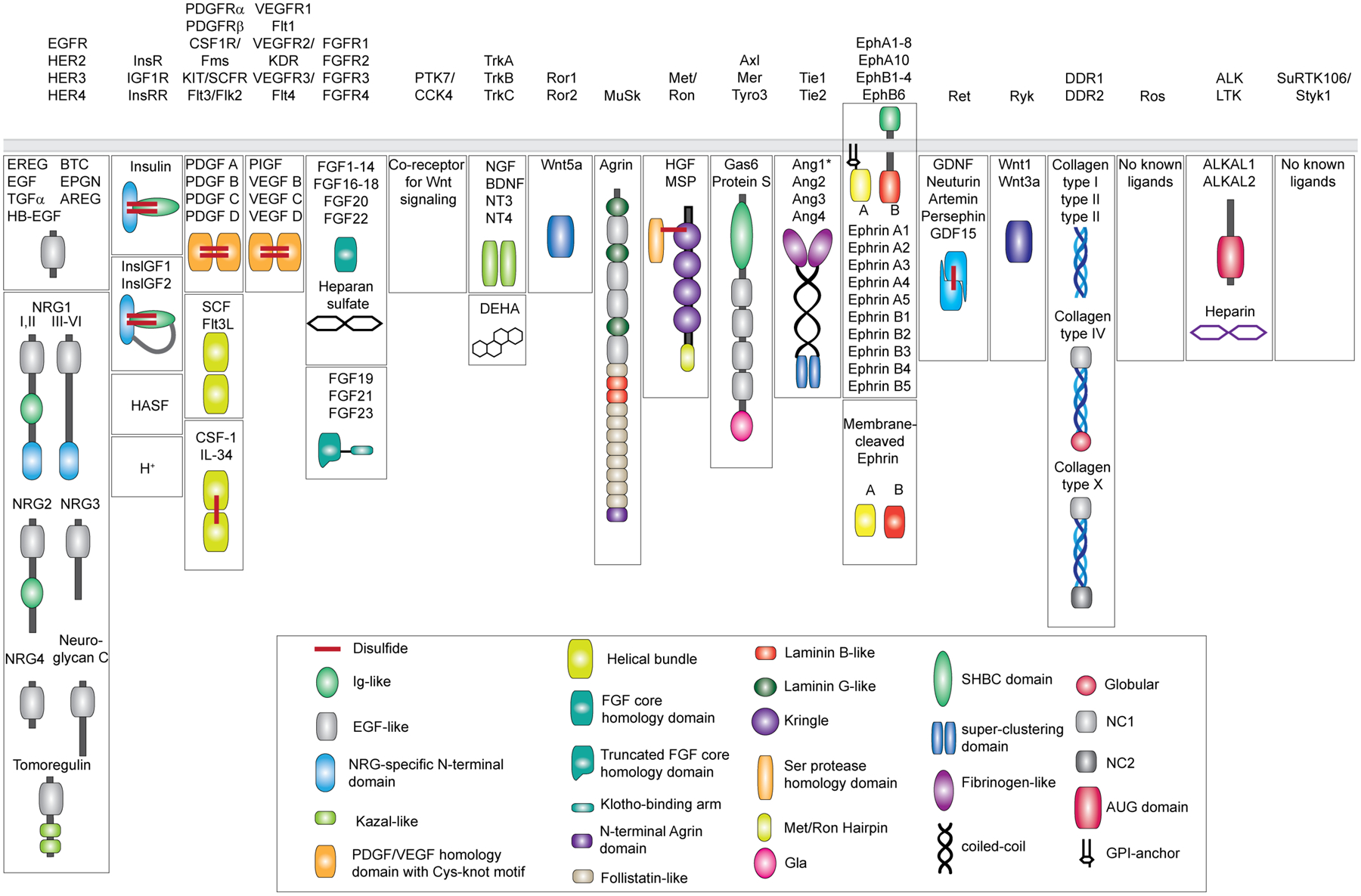
RTKs are shown on the top categorized into 19 different families as originally described [1] and recently revised to remove the LMR1–3 family due to its re-classification as Ser/Thr receptor kinases [127]. Ligands for each RTK family are shown underneath in mature, secreted form. All membrane-tethered ligands are cleaved off the membrane except for ephrins, which activate their cognate receptors in a juxtacrine fashion. The ligands are drawn with their N-terminus pointing away from the membrane. Main structural domains are depicted in a cartoon form in their known oligomeric state except for Angiotensins*, which may form higher-order oligomers in addition to dimers. If applicable, domain labels are included as captions. Sizes of individual domains are not drawn up to scale.
