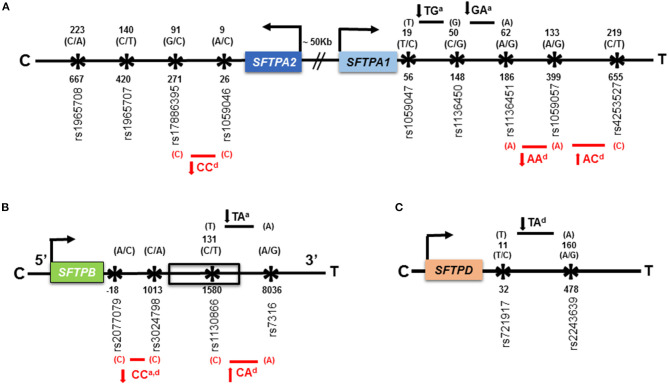
Figure 3.
Association of haplotypes of the SFTPA1, SFTPA2, SFTPB, and SFTPD genes with HP compared to avian antigen exposed and non-exposed controls in the two-SNP haplotype estimation model. (A) is a schematic representation of SNPs of the SFTPA1 and SFTPA2 genes. The distance between the genes is ~50 kb shown with sign “//.” The studied SNPs are located within exons. (B) is a schematic representation of the SFTPB gene shown in 5' to 3' UTR direction. Only rs1130866 of the SFTPB shown in box, is located within an exon and the corresponding amino acid (AA) is shown above that. The SFTPB (1) rs2077079 is located 10 nucleotides downstream of TATAA box, in the 5′ regulatory region; (2) rs3024798 is located in the intron; and (3) rs7316 is located in the 3′UTR. Thus, no AA is shown for these SNPs. (C) is a schematic representation of SNPs of the SFTPD gene. The studied SNPs are located within exons. The gene direction is shown from centromere (C) to telomere (T) and the arrow above the color box indicates transcriptional orientation. The number above the black arrow indicates the AA number and the corresponding nucleotide change for that particular SNP is shown in parenthesis. The numbering of AAs in SFTPA2, SFTPA1, and SFTPB is based on the sequence of the precursor molecule, whereas, it is based on the mature protein (i.e., minus the signal peptide) in SFTPD. The numbers below the black arrow indicate the nucleotide number and the corresponding SNP ids. The transmitted haplotypes and nucleotide changes are shown in bold. The haplotypes associated with HP risk compared to avian antigen exposed and non-exposed controls are shown in red font with red line and black font with black line, respectively. The direction of the solid arrows besides haplotypes indicates increased or decreased HP risk compared to control groups. The superscript “a” and “d” after a given haplotype indicates additive and dominant effect, respectively, of that particular haplotype.