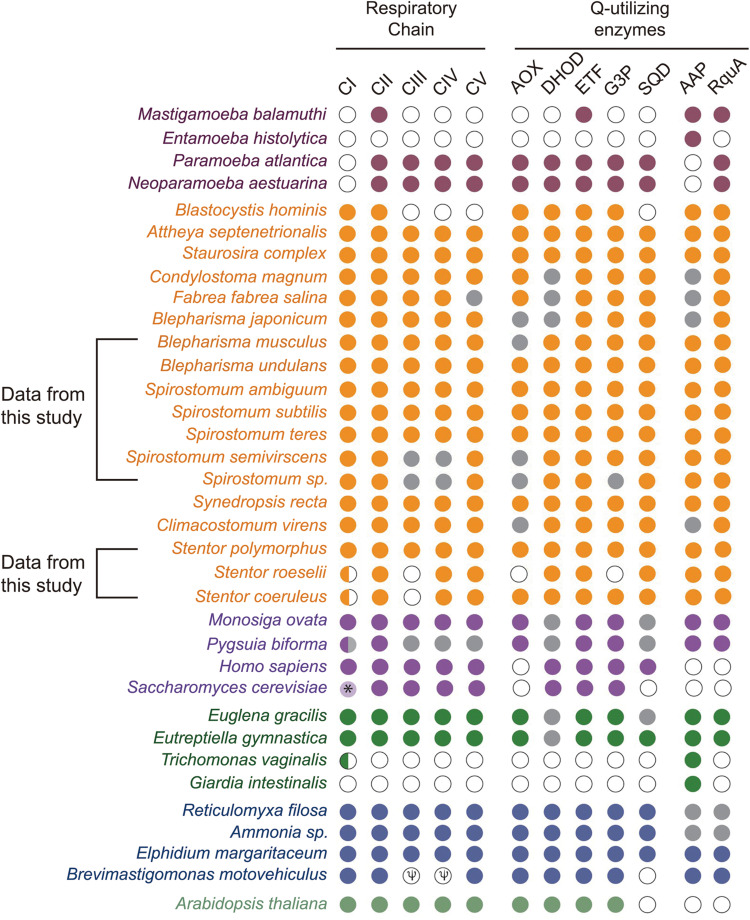
FIGURE 6.
Co-occurrence and distribution of quinone-utilizing enzymes and RquA in the transcriptomes and genomes from Eukaryotes. This figure is based on previously published data (Figure 3; Stairs et al., 2018) and with additional information from Spirostomum, Blepharisma and Stentor spp., on respiratory chain elements (Complexes I–V, CI–CV), AOX (alternative oxidase), DHOH (dihydroorotate dehydrogenase), ETF (electron-transferring flavoprotein system components), G3P (glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, G3PDH), SQO (sulfite:quinone oxidoreductase), RquA, and AAP (indicates one or more anaerobiosis-associated proteins). Colored plots indicate presence and absences of proteins or protein subunits associated with anaerobic systems in Eukaryotes (maroon, Amoebozoa; yellow, Stramenopiles and Alveolata; mauve, Obazoa; green, Excavata; blue-gray, Rhizaria; dull-green, Archaeplastida). Gray and white circles indicate no homologs of above mentioned proteins in transcriptome and genome data, respectively; while, half circle indicates the presence of only two subunits (NUOE and NUOF) in CI complex; while “Ψ” indicates pseudogenes in the species.