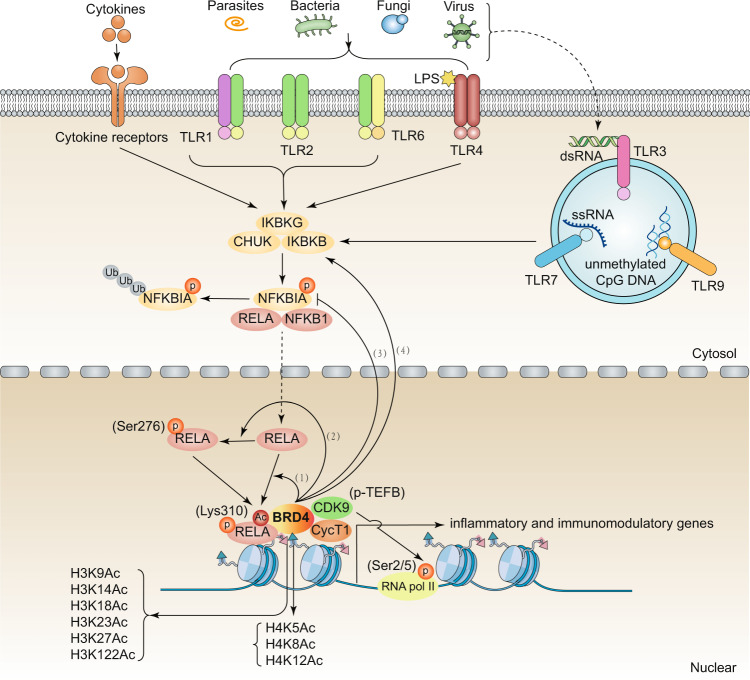
Fig. 2.
The role BRD4 in regulating the NF-κB pathway in inflammation and immunity. BRD4 regulates the activation of the NF-κB pathway caused by TLR ligands through at least four pathways: (1) BRD4 directly acetylates RELA through its atypical histone acetyltransferase activity; (2) BRD4 directly promotes the phosphorylation of RELA; and (3–4) BRD4 promotes the phosphorylation of RELA through inhibiting the translation of NFKBIA and increasing the phosphorylation of NFKBIA and IKBKB. Abbreviations: CDK9, cyclin-dependent kinase 9; CHUK, component of inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase complex; CycT1, cyclin T1; IKBKB, inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase regulatory subunit beta; IKBKG, inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase regulatory subunit gamma; NFKBIA, NFKB inhibitor alpha; NFKB1, nuclear factor kappa B subunit 1; p-TEFb, positive transcription elongation factor b; RELA, RELA proto-oncogene; RNA pol II, RNA polymerase II; TLR, toll-like receptor (numbers 1–9)