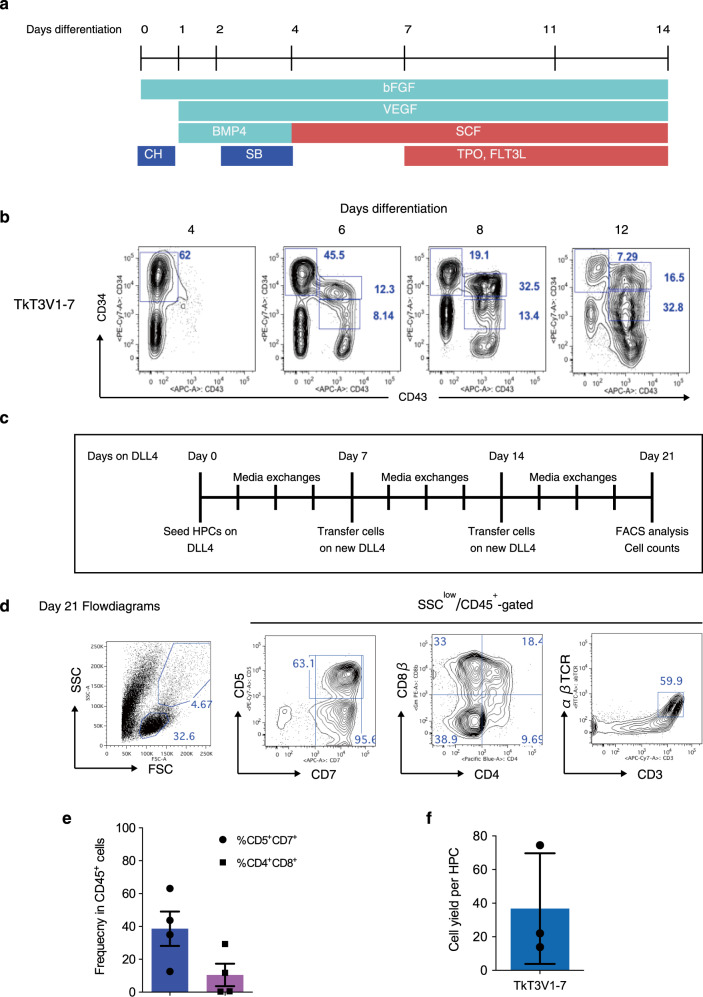
Fig. 1. Generation of CD4+CD8αβ+ DP T-cells from T-iPSCs in feeder-free (Ff) culture conditions.
a Scheme of hematopoietic induction from T-iPSC clones. EBs were generated from a single-cell dissociated human T-iPSCs proliferated in a feeder- and serum-free condition and induced to differentiate into mesoderm and later into hematopoietic cells in the presence of CH, BMP-4, bFGF, and VEGF. The emerging hematopoietic cells were proliferated in the presence of hematopoietic cytokines. SB was added on day 2 to induce definitive hematopoiesis. CH, CHIR99021; SB, SB431542. b Representative kinetic analysis of hematopoietic differentiation from a T-iPSC clone, TkT3V1-7, assessed based on the expression levels of CD34 and CD43 at the indicated days after induction (n = 3). c Schedule of T-cell differentiation of T-iPSC-HPCs in immobilized-DL4 and retronectin culture plates. d Representative flow cytometry plots of T-iPSC-HPCs differentiated on DL4 and RN cultures in the presence of SCF, TPO, FLT3L, and IL-7 for 21 days (n = 4). e Frequencies of CD5+CD7+ progenitor T-cells (blue) and CD4+CD8αβ+ DP-cells (purple) generated from T-iPSC-HPCs 21 days after differentiation on DL4 and RN cultures (n = 4). f DL4 and RN cell yields after 21 days of culture normalized to the input T-iPSC-HPC numbers (n = 3). Data represent mean ± SD of n independent experiments.