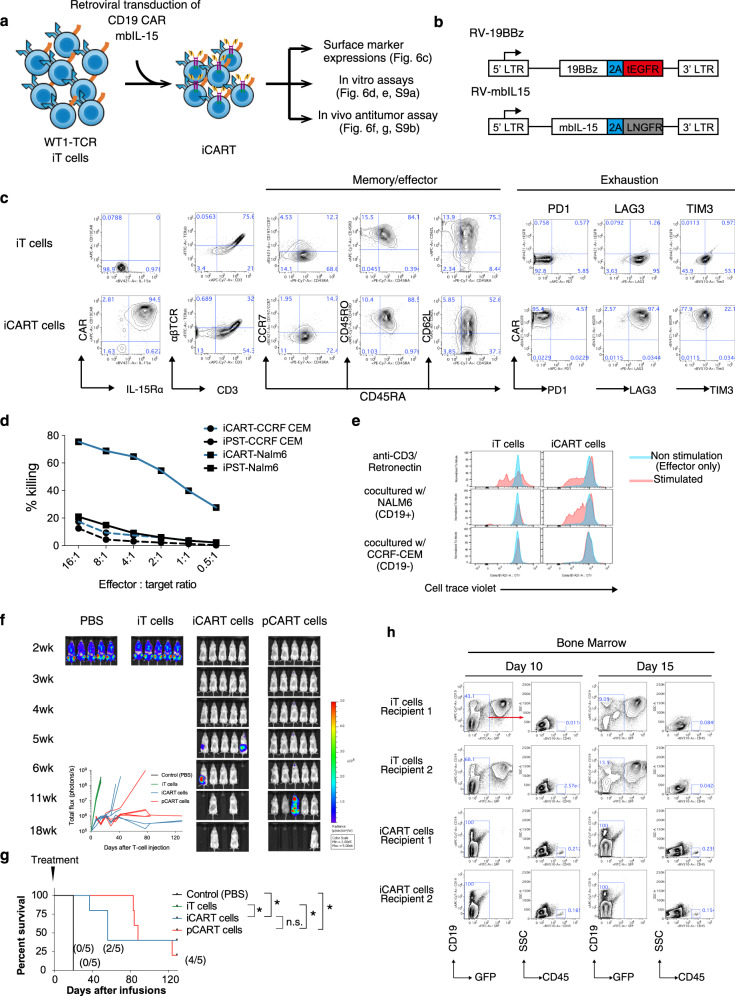
Fig. 6. In vitro and in vivo functions of iCART cells.
a A schematic showing generation and assessment of iCART cells from iT cells. b Designs of RV-19BBz CAR (top) and RV-mbIL-15 (bottom). This design allows the co-expression of the CAR and truncated EGFR and mbIL-15 and LNGFR from the same LTR promoter by using a self-cleaving P2A sequence. LTR, long terminal repeat, Porcine teschovirus self-cleaving 2A sequence. c Representative flow cytometry plots of untransduced and 19BBz-transduced iT cells (iCART cells) showing expression levels of CD19 CAR, IL-15Rα, CD3, αβTCR, CD8α, CD8β (left), naive/memory T-cell markers (middle), and exhaustion markers (right). d Cytotoxic activity of iT cells and iCART cells using CD19+ NALM-6 and CD19- CCRF-CEM as target cells. Data represent two independent experiments. e Representative histograms showing cell divisions of CellTrace Violet-labeled iT cells (left) and iCART cells (right) cocultured with CD19 + NALM-6 or CD19- CCRF-CEM (red) or without target cells (blue) for 6 days. Cell divisions of iT cells and iCART cells activated by retronectin/CD3 conditions are shown (top panels). Data represent two independent experiments. f, g In vivo anti-tumor activity of iT cells and iCART cells in a systemic tumor model. NOG mice were intravenously inoculated with NALM-6-expressing luciferase 4 days before treatment, treated once intravenously with PBS, 1 × 107 iT-cells, iCART-cells, or primary CART-cells, and monitored for (f) tumor volume and (g) survival rate (n = 5 mice each). Values in parentheses represent the fraction of mice without tumor relapse. h NALM-6-bearing mice were treated with 1 × 107 iT cells or iCART cells. At 10 and 15 days after treatment, mice were euthanized and bone marrow cells were collected. Presence of iT cell or iCART cells (GFP-CD19-humanCD45+) and NALM-6 (GFP+CD19+) cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. *P < 0.05 (log-rank Mantel–Cox test with Bonferroni corrections, two-tailed).