Figure 6.
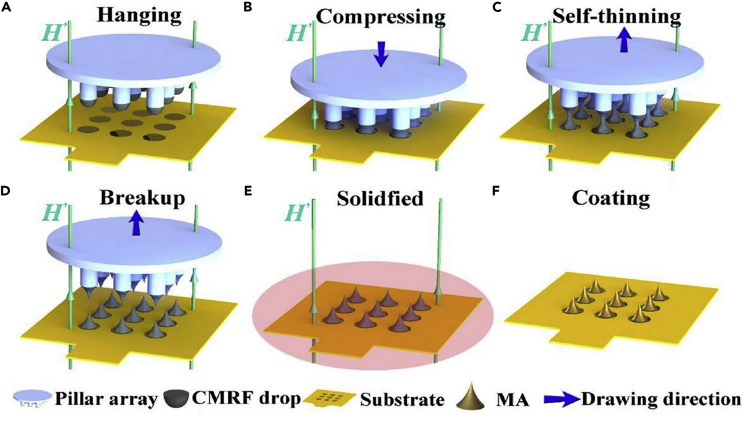
Sequential steps of microneedles (MNs) fabrication by magneto-rheological drawing lithography (MRDL), an additive manufacturing method
(A) Pillar tips, with a diameter of 700 μm, were coated by dipping in curable magnetorheological fluid (CMRF).
(B) Then, the pillars were moved downward, toward a substrate, with a constant speed of 1.5 mm/s to press droplets to the substrate for 1 s.
(C) Pillars moved upward with the speed of 1.5 mm/s and stopped in 12 mm from the substrate, resulting in a necking effect.
(D and E) When the thinned CMRF lines broke up at room temperature, the MNs were solidified at 100°C for 1 h.
(F) Subsequently, the fabricated MNs were coated by titanium (Ti) and gold (Au) using a magnetron sputtering machine (Ren et al., 2017). Adapted with permission from (Ren et al., 2017). Copyright 2017, Elsevier.