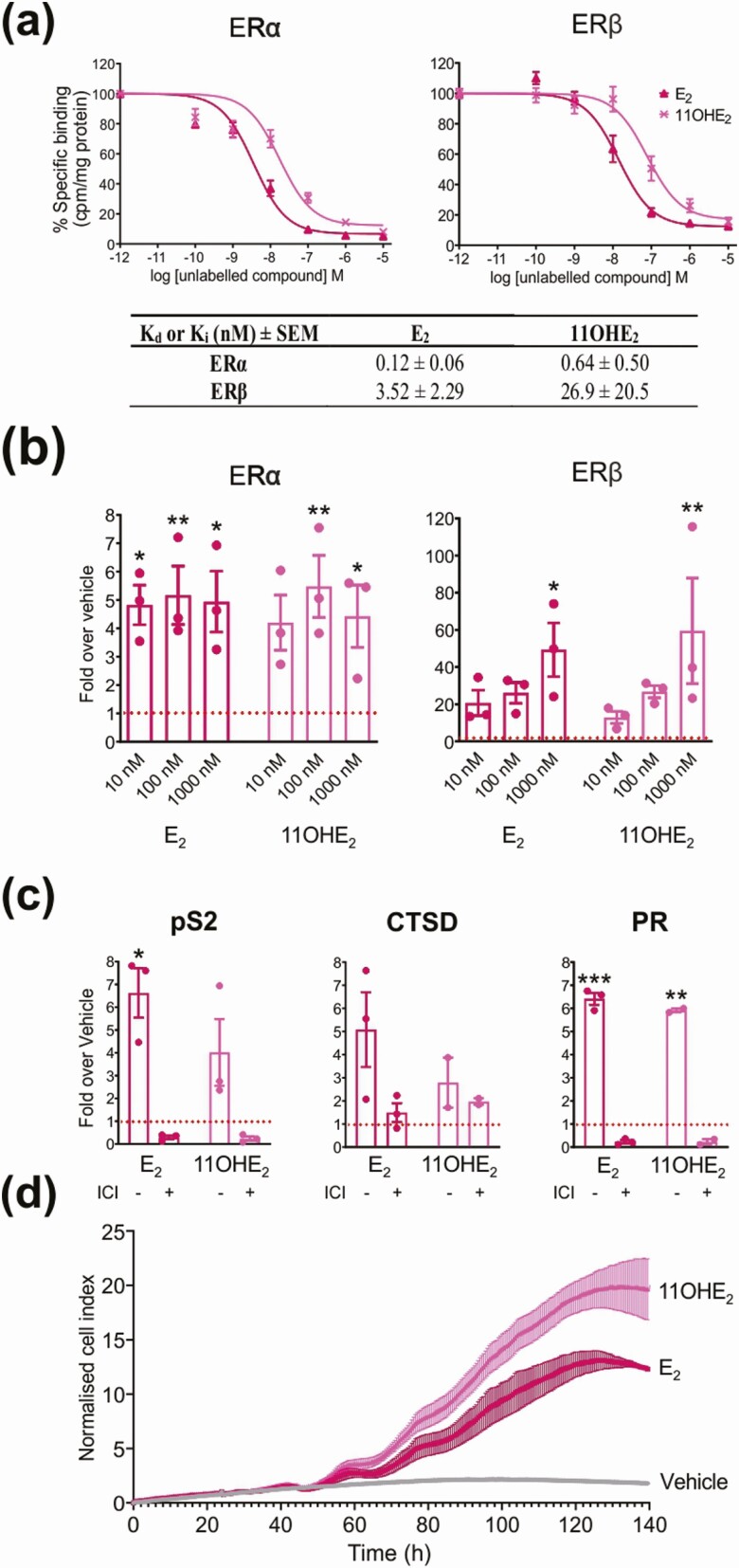
Figure 2.
11-Oxygenated estrogens bind and activate the human estrogen receptors α and β. A, Binding affinities of 11β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol (11OHE2) relative to 17β-estradiol (E2) as determined by whole-cell binding assays (n = 3). Binding data were analyzed with nonlinear regression assuming competitive binding to one class of binding sites, and the Ki ± SEM values for 11OHE2 determined from a heterologous displacement curve. B, Transactivation of human estrogen receptor α (Erα) and ERβ by 11OHE2 and E2 (n = 3). *P less than .05; **P less than .005; one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, compared to the vehicle control set as 1. C, Induction of ER-regulated gene expression (pS2, estrogen-responsive pS2 gene; CTSD, cathepsin D; PR, progesterone receptor) in MCF7-BUS cells by 1-nM 11OHE2 and E2 in the absence and presence of 1-µM fulvestrant (ICI). *P less than .05; **P less than .005; and ***P less than .001; one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, compared to the vehicle control set as 1. D, Real-time proliferation of MCF7-BUS cells as induced by 1-nM 11OHE2 and E2 (n = 3). All results are represented as mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments, each performed in triplicate.