Figure 4. Effects of CIE on spine morphology of PrL-L5 pyramidal neurons.
A, Adapted criteria for 4 types of spines from Spiga et al, 2014 (Spiga et al., 2014) and example spines for each type.
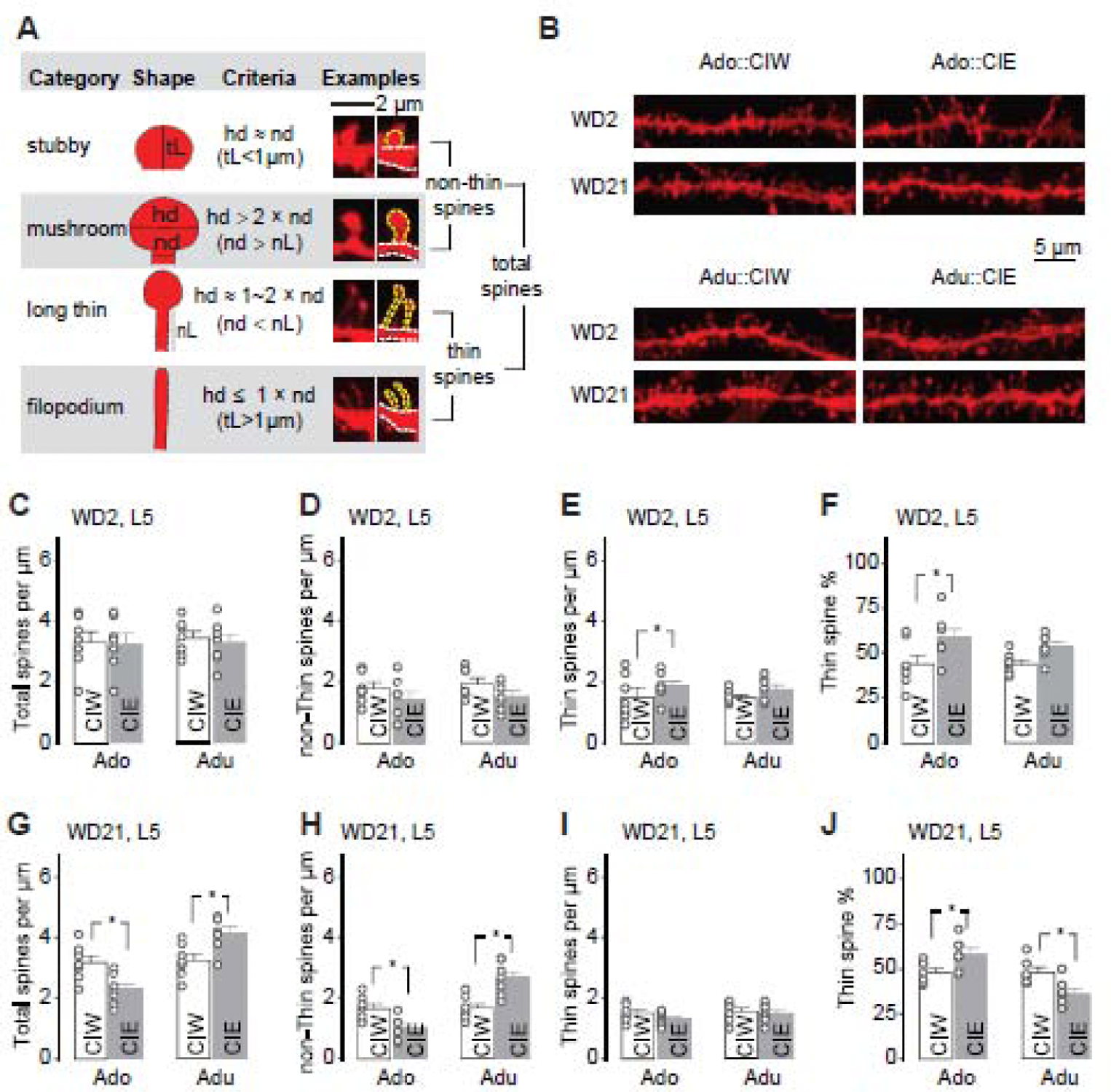
B, Example DiI-stained spines in PrL-L5 pyramidal neurons 2 and 21 days after CIW or CIE treatment during the adolescent and early-adult stages, respectively.
C–F, Summarized data showing the spine density of total spines (C), non-thin spines (D) and thin spines (E), as well as the thin spine % among total spines (F) 2 days after CIW or CIE treatment. Neither CIE treatment nor the age factor significantly affected total spine density (C, CIW/CIE × Ado/Adu interaction F1,24<0.1, p=0.84, CIW/CIE F1,24=0.1, p=0.74, Ado/Adu F1,24=0.1, p=0.78), non-thin spine density (D, CIW/CIE × Ado/Adu interaction F1,24<0.1, p=0.85, CIW/CIE F1,24=5.5, p=0.03, Ado/Adu F1,24=1.0, p=0.32), or thin spine density (E, CIW/CIE × Ado/Adu interaction F1,24=0.2 p=0.48, CIW/CIE F1,24=3.1, p=0.09, Ado/Adu F1,24=0.32, p=0.58). CIE treatment, but not the age factor, significantly affect the thin spine ratio (F, CIW/CIE × Ado/Adu interaction F1,24=0.4, p=0.54, CIW/CIE F1,24=9.8, p<0.01, Ado/Adu F1,24=0.4, p=0.54)
G–J, Summarized data showing the spine density of total spines (G), non-thin spines (H) and thin spines (I), as well as the thin spine % among total spines (J) 21 days after CIW or CIE treatment. Total spine density was decreased after Ado::CIE but increased after Adu::CIE (G, CIW/CIE × Ado/Adu interaction F1,24=18.4, p<0.01, CIW/CIE F1,24<0.1, p=0.95, Ado/Adu F1,24=21.4, p<0.01). Similarly, Ado::CIE and Adu::CIE significantly decreased and increase the non-Thin spine density, respectively (H, CIW/CIE × Ado/Adu interaction F1,24=24.8, p<0.01, CIW/CIE F1,24=0.9, p=0.36, Ado/Adu F1,24=26.1, p<0.01). No significant differences of thin spine density were observed between CIW vs. CIE treatments or between Ado vs. Adu age groups (I, CIW/CIE × Ado/Adu interaction F1,24=0.5 p=0.48, CIW/CIE F1,24=1.7, p=0.20, Ado/Adu F1,24=1.4, p=0.25). Thin spine ratio was increased after Ado::CIE but decreased after Adu::CIE (J, CIW/CIE × Ado/Adu interaction F1,24=15.8, p<0.01, CIW/CIE F1,24=0.1, p=0.72, Ado/Adu F1,24=15.4, p<0.01).
Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA (C–J), followed by Bonferroni post-hoc tests. Data collections were made on 7 rats in each group.
