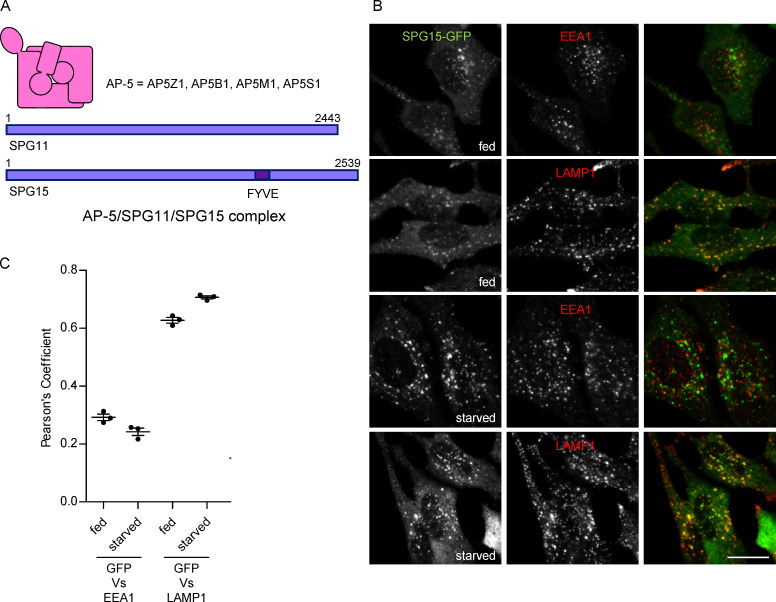
Figure 1.
Starvation-enhanced recruitment of AP-5/SPG11/SPG15 to late endosomes/lysosomes. (A) Schematic diagram of the components of the AP-5/SPG11/SPG15 complex. The structure of AP-5 is assumed to be similar to the structures of the other AP complexes, and the complex has a combined molecular weight of ∼260 kD. The structures of SPG11 and SPG15 are unknown, but each of these proteins is larger than the entire AP-5 complex, with molecular weights of ∼280 kD and ∼285 kD, respectively. (B) IF labeling of a cell line stably expressing SPG15-GFP (originally created by bacterial artificial chromosome TransgeneOmics; Słabicki et al., 2010). The GFP signal was amplified with anti-GFP, and cells were double labeled for either EEA1 as a marker for early endosomes or LAMP1 as a marker for late endosomes/lysosomes, under either fed or starved conditions (1 h). In this figure and all subsequent figures, starvation was performed in PBS (+Mg+Ca) unless otherwise indicated. Scale bar: 20 µm. (C) Quantification of the colocalization between SPG15-GFP and either EEA1 or LAMP1, using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. The experiment was performed in biological triplicate (mean indicated; n = 3), and 20 cells were quantified per condition. Error bars represent SEM.