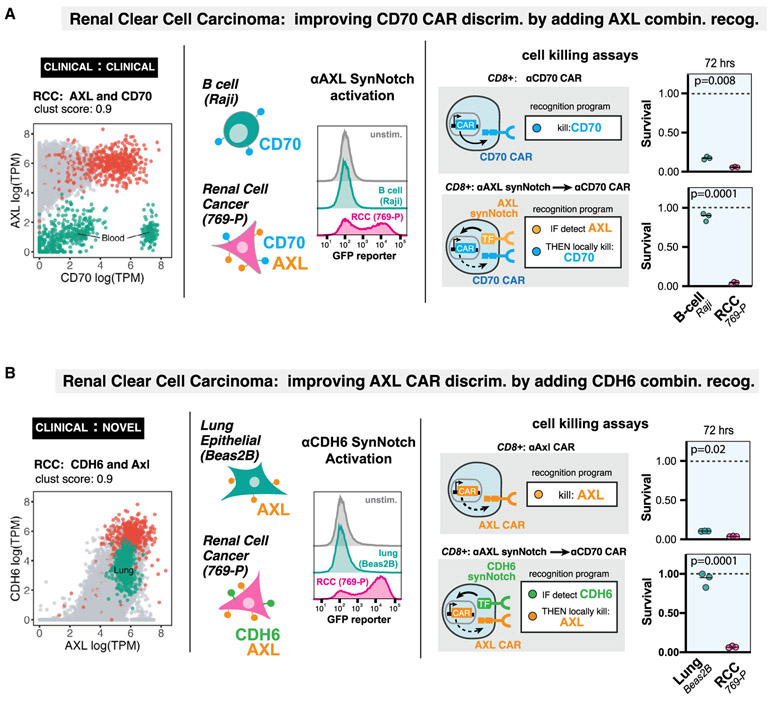
Figure 4. Computationally Predicted Antigen Pairs Can Be Constructed as AND-Gated CAR T Cells in a Laboratory Setting, with Precise In Vitro Discrimination.
(A) RCC recognition circuit: CD70 and AXL. Segregation of RCC samples (red points) versus normal tissue samples (gray points) in antigen expression space, highlighting overlap of CD70 expression with normal blood samples (green points). We constructed an anti-AXL synNotch receptor and validated that human T cells expressing the receptor can detect 769-P renal cell cancer cell line (CD70+AXL+), but not Raji B cell line (CD70+AXL−)via FAC detection of GFP reporter induction. In cell killing assays, we compared human primary CD8+ T cells constitutively expressing the anti-CD70 CAR with the same cells transfected with the anti-AXL synNotch driving anti–CD70 CAR AND-gate circuit. The single antigen targeting anti-CD70 CAR T cells killed both RCC and B cell lines, while the circuit T cells selectively killed RCC cells (n = 3, p value from unpaired two sample student’s t test).
(B) RCC recognition circuit: AXL and CDH6. Segregation of RCC samples (red points) versus normal tissue samples (gray points) in antigen expression space, highlighting overlap of AXL expression with normal lung samples (green points). We constructed an anti-CDH6 synNotch receptor and validated that human T cells expressing the receptor can detect 769-P renal cell cancer cell line (AXL+CDH6+), but not the Beas2B lung epithelial cell line (AXL+CDH6−)via FAC detection of GFP reporter induction. In cell killing assays, we compared human primary CD8+ T cells constitutively expressing the anti-AXL CAR with the same cells transfected with the anti-CDH6 synNotch driving anti–AXL CAR AND-gate circuit. The single antigen targeting anti-AXL CAR T cells killed both RCC and lung cell lines, while the circuit T cells selectively killed RCC cells (n = 3, p value from unpaired two sample student’s t test).