Figure 8.
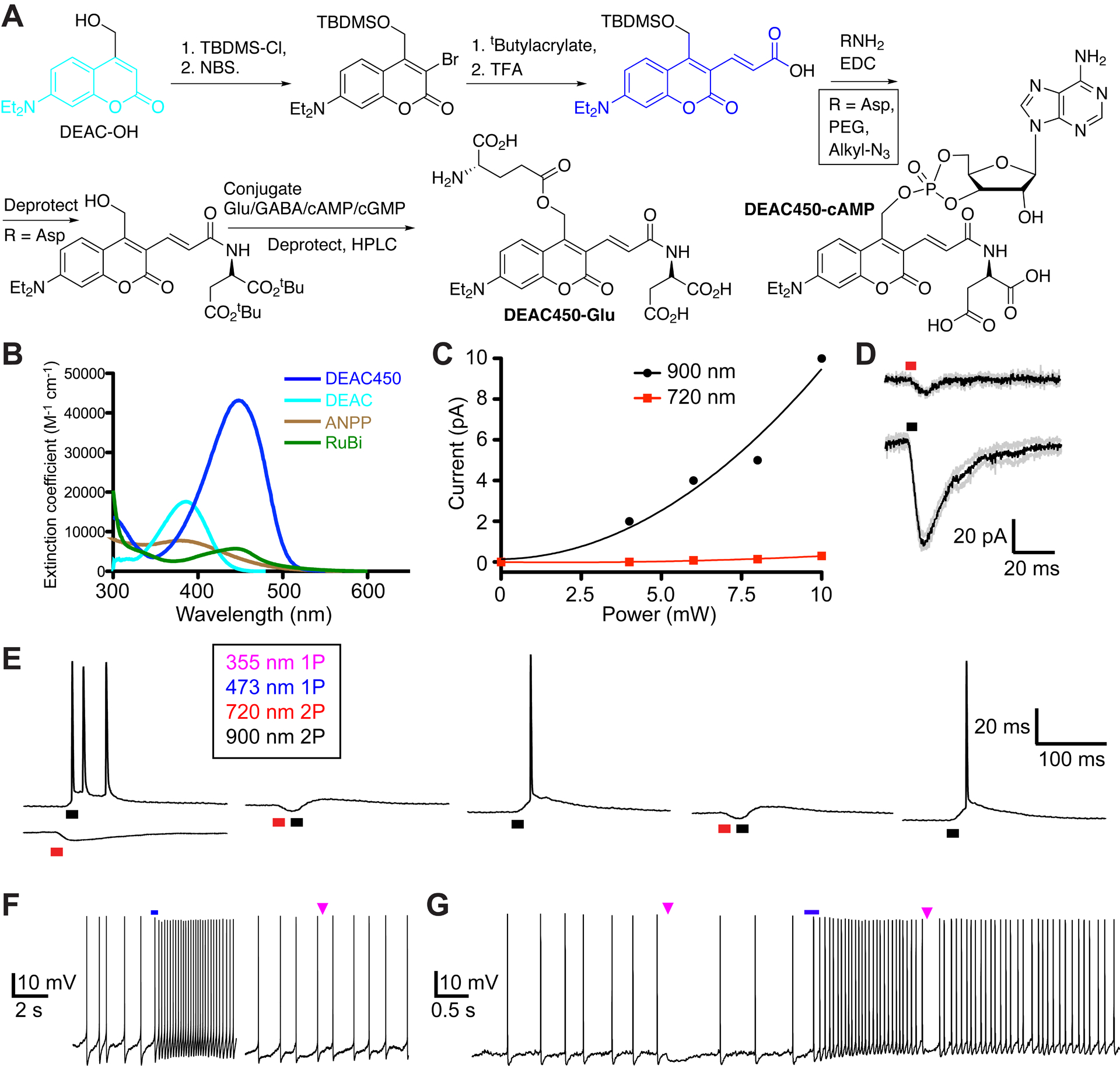
DEAC450 – enables wavelength selective, orthogonal photo-actuation with living cells.
A. Synthetic outline for the conversion of DEAC into DEAC450. Intermediate 3 is suitably bifunctional for coupling of a variety of “solubilization units” on its acid functionality, followed by coupling of the biomolecule to the subsequently deprotected methylalcohol. B. Absorption spectra of DEAC and DEAC450, with two other blue absorbing nitrobenzyl chromophores65,66. Only DEAC450 has a real minimum at 350 nm, the wavelength where traditional caged compounds are very sensitive. C. Comparison of 2P uncaging of DEAC450Glu with increasing power at 900 nm versus 720 nm67. D. Uncaging at 720 nm high powers were required to evoke detectable responses, such powers at 900 nm generated very large currents68. E. Co-application of DEAC450-Glu and CDNI-GABA allowed 2-color, 2P uncaging on CA1 neurons. Action potentials could be generated and blocked in a wavelength-selective manner. F. DEAC450-cAMP uncaged inside neurons with blue light enhances the firing rate, whereas UV light evokes no response. G. Wavelength-selective 1P UV uncaging of CDNI-GABA blocks spikes, followed by 1P-blue uncaging of cAMP enhances tonic firing, which is blocked by UV. D,E: Reproduced with permission from ref. 68. Copyright (2015) Wiley. F: Adapted with permission from ref. 69. Copyright (2013) ACS.
