FIGURE 9.
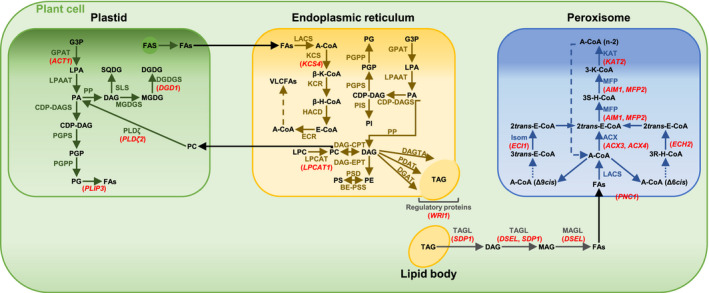
Candidate genes for lipid metabolism and their involvement in glycerolipid biosynthesis and fatty acid β‐oxidation. Overview of prokaryotic and eukaryotic glycerolipid biosynthesis pathways and fatty acid β‐oxidation in the plastid, in or at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and in the peroxisome, showing the interconversion of pathways. Candidate genes differentially regulated between PZ and AZ are represented in red, except PES1 and pPLAIIIβ. Abbreviations: A‐CoA: acyl‐CoA; ACX: acyl‐CoA thioesterase; β/3R/3S‐H‐CoA: β/3R/3S‐hydroxyacyl‐CoA; β/3‐K‐CoA: β/3‐ketoacyl‐CoA; BE‐PSS: base‐exchange‐type phosphatidylserine synthase; CDP‐DAGS: CDP‐DAG synthase; CoA: coenzyme A; DAG: diacylglycerol; DAGTA: diacylglycerol transacylase; DAG‐CPT: CDP‐choline: diacylglycerol cholinephosphotransferase; DAG‐EPT: CDP‐ethanolamine:diacylglycerol cholinephosphotransferase; DGAT: diacylglycerol acyltransferase; DGDG: digalactosyldiacylglycerol; DGDGS: digalactosyldiacylglycerol transferase; E‐CoA: enoyl‐CoA; ECR: enoyl‐CoA reductase; FAS: fatty acid synthase; FAs: fatty acids; G3P: glycerol 3‐phosphate; GPAT: glycerol‐3‐phosphate acyltransferase; HACD: hydroxyacyl‐CoA dehydratase; Isom: isomerase; KAT: 3‐ketothiolase; KCR: ketoacyl‐CoA reductase; KCS: 3‐ketoacyl‐CoA synthase; LACS: long‐chain acyl‐CoA synthetase; LPA: lysophosphatidic acid; LPAAT: lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase; LPC: lysophosphatidylcholine; LPCAT: lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase; MAG: monoacylglycerol; MAGL: monoacylglycerol lipase; MFP: multifunctional protein; MGDG: monogalactosyldiacylglycerol; MGDGS: monogalactosyldiacylglycerol transferase; PA: phosphatidic acid; PC: phosphatidylcholine; PDAT: phospholipid:diacylglycerol acyltransferase; PE: phosphatidylethanolamine; PG: phosphatidylglycerol; PGP: phosphatidylglycerol phosphate; PGPP: phosphatidylglycerol phosphate phosphatase; PGPS: phosphatidylglycerol phosphate synthase; PI: phosphatidylinositol; PIS: PI synthase; PP: phosphatidate phosphatase; PS: phosphatidylserine; PSD: phosphatidylserine decarboxylae; SLS: sulfolipid synthase; SQDG: sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol; TAG: triacylglycerol; TAGL: triacylglycerol lipase; VLCFAs: very long‐chain fatty acids. Adopted from Li‐Beisson et al. (2013). Candidate genes: ACT1, ACYLTRANSFERASE 1, ACX3, ACYL‐COA OXIDASE 3, ACX4, ACYL‐COA OXIDASE 4, AIM1, ABNORMAL INFLORESCENCE MERISTEM 1, DGD1, DIGALACTOSYL DIACYLGLYCEROL DEFICIENT 1, DSEL, DAD1‐LIKE SEEDLING ESTABLISHMENT‐RELATED LIPASE, ECH2, ENOYL‐COA HYDRATASE 2, ECI1, Δ3, Δ2‐ENOYL COA ISOMERASE 1, KAT2, 3‐KETOACYL‐COA THIOLASE 2, KCS4, 3‐KETOACYL‐COA SYNTHASE 4, LPCAT1, LYSOPHOSPHATIDYLCHOLINE ACYLTRANSFERASE 1, MFP2, MULTIFUNCTIONAL PROTEIN 2, PES1, PHYTYL ESTER SYNTHASE 1, PLDζ2, PHOSPHOLIPASE D ζ 2, PLIP3, PLASTID LIPASE 3, PNC1, PEROXISOMAL ADENINE NUCLEOTIDE CARRIER 1, pPLAIIIβ, PATATIN‐RELATED PHOSPHOLIPASE A IIIβ, SDP1, SUGAR‐DEPENDENT1, WRI1, WRINKLED 1. Acyl‐CoA chains with a cis double bond on an even‐numbered carbon are exemplified by Δ6cis, while fatty acids with cis double bonds at odd‐numbered positions are exemplified by Δ9cis
