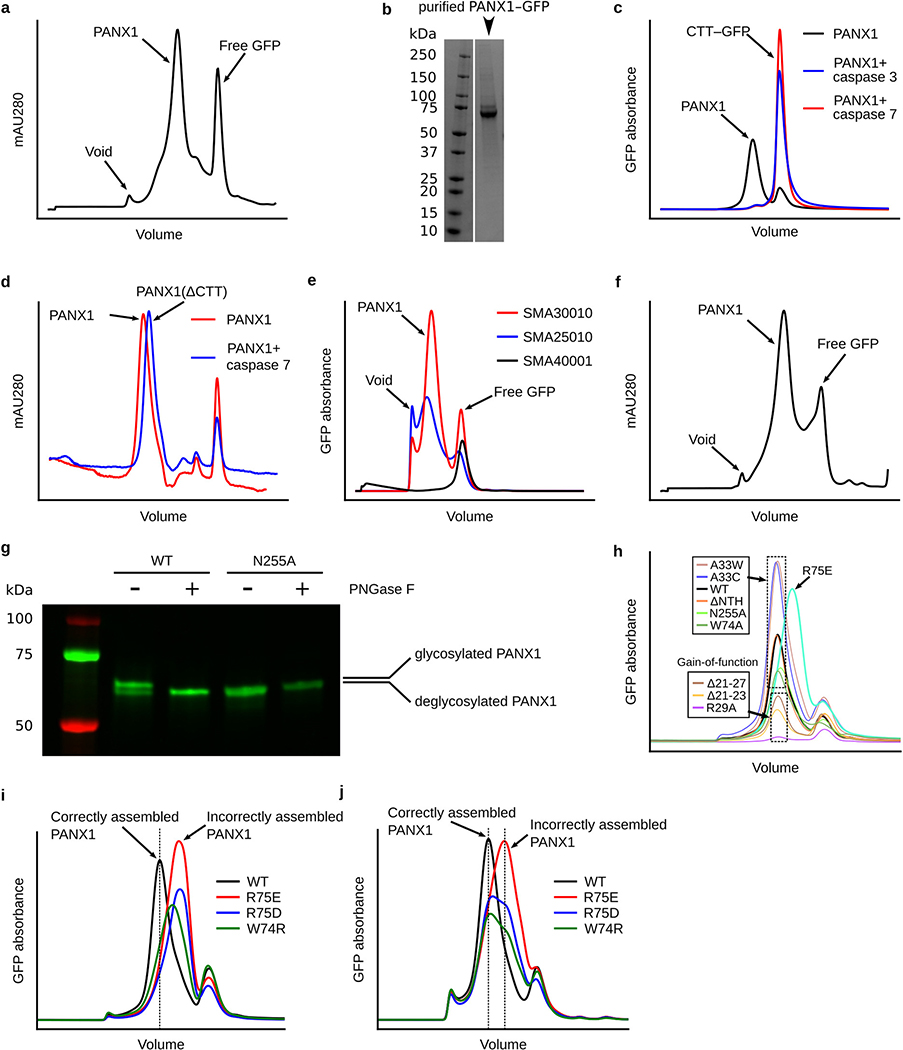
Extended Data Figure 1: Purification and biochemical analysis of hsPANX1.
a, Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) profile of wt-hsPANX1 purification using glyco-diosgenin (GDN). b, SDS gel of purified wt-hsPANX1-GFP (For gel source data, see Supplementary Figure 1a for gel source data). c, Fluorescence size-exclusion chromatography (FSEC) experiment on caspase 3/7 cleavage of wt-hsPANX1-GFP. GFP absorbance (480 nm) is shown in y-axis. d, Caspase 7 cleavage of purified wt-hsPANX1-GFP. The cleavage of CTT results in a peak shift. Tryptophan absorbance (280 nm) is shown in y-axis. e, Styrene maleic acid (SMA) solubilization screening of wt-hsPANX1 using FSEC. Three SMA polymers (SMA25010, SMA30010, and SMA40001) were tested. GFP absorbance (480 nm) is shown in y-axis. f, SEC profile of hsPANX1 purification using SMA30010. Tryptophan absorbance (280 nm) is shown in y-axis. g, Deglycosylation test of wt-hsPANX1-GFP and N255A-hsPANX1-GFP using PNGase F. Bands correspond to the glycosylated and non-glycosylated hsPANX1 are marked. See Supplementary Figure 1b for gel source data. h, FSEC analysis on the hsPANX1 mutations with electrophysiology data. Cells expressing hsPANX1 WT or mutants are solubilized using GDN. Gain-of-function mutations with less expression level are labeled. R75E mutant contains a peak position shifted to the right. i and j, FSEC analysis on extracellular gate mutations of hsPANX1 solubilized using GDN (i) or SMA30010 (j). Peak positions of correctly assembled hsPANX1 and incorrectly assembled hsPANX1 are indicated by arrows and vertical bars. The W74R, R75D, and R75E showed decreased stability relative to wild-type because, when extracted using detergent, they mostly ran at positions representing incorrect assemblies (i). Nevertheless, the SMA-extracted W74R, R75D, and R75E all showed peaks at positions representing correct assemblies (j), indicating that they are able to form correctly assembled channel complex in a native lipid environment.