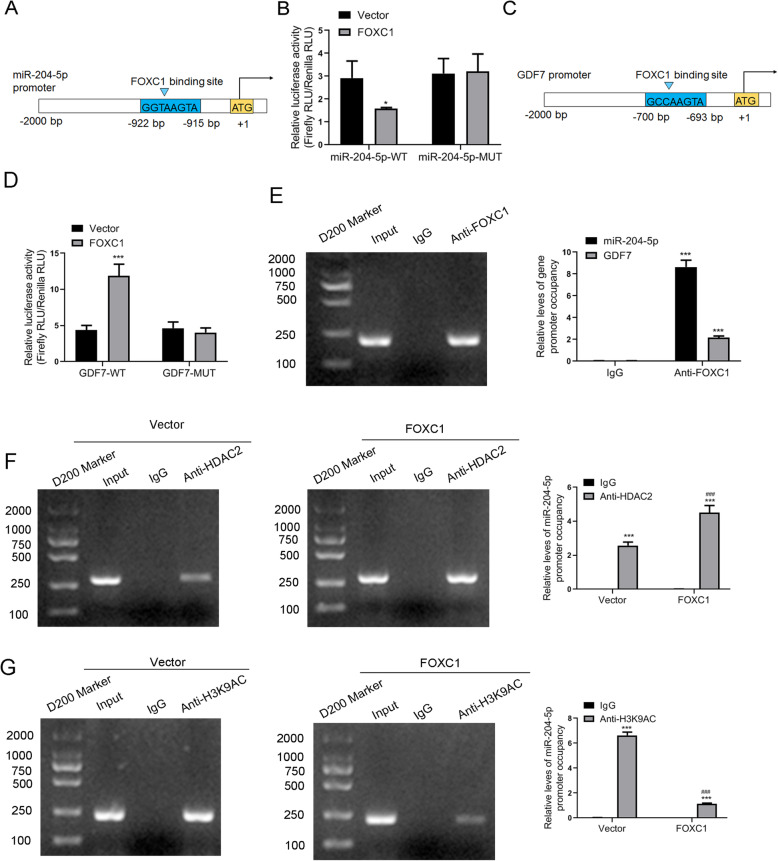
Fig. 8.
FOXC1, as a transcription factor, binds to the promoter of miR-204-5p and GDF7. a Predicted binding site of FOXC1 (GGTAAGTA) in the miR-204-5p promoter (− 922 to − 915 bp). b Relative luciferase activity of cells transfected with vector/vector-FOXC1 and miR-204-5p-WT or vector/vector-FOXC1 and miR-204-5p-MUT. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05 (n = 3 independent experiments). c Predicted binding site of FOXC1 (GCCAAGTA) in the GDF7 promoter (− 700 to − 693 bp). d Relative luciferase activity of cells transfected with vector/vector-FOXC1 and GDF7-WT or vector/vector-FOXC1 and GDF7-MUT. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. ***p < 0.001 (n = 3 independent experiments). e The enrichment of FOXC1 in the promoter of GDF7 (left and right panel) and miR-204-5p (right panel) was measured by gel electrophoresis and ChIP assay. Normal IgG was used as a negative control. f The enrichment of histone deacetylase HDAC2 in the promoter of miR-204-5p was measured by gel electrophoresis and ChIP assay. g The enrichment of histone acetylase H3K9AC in the promoter of miR-204-5p was measured by gel electrophoresis and ChIP assay. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. ***anti-HDAC2 or anti-H3K9AC vs IgG, ###overexpression of FOXC1 vs vectors in HDAC2 or H3K9AC samples. ***p < 0.001, ###p < 0.001 (n = 3 independent experiments)