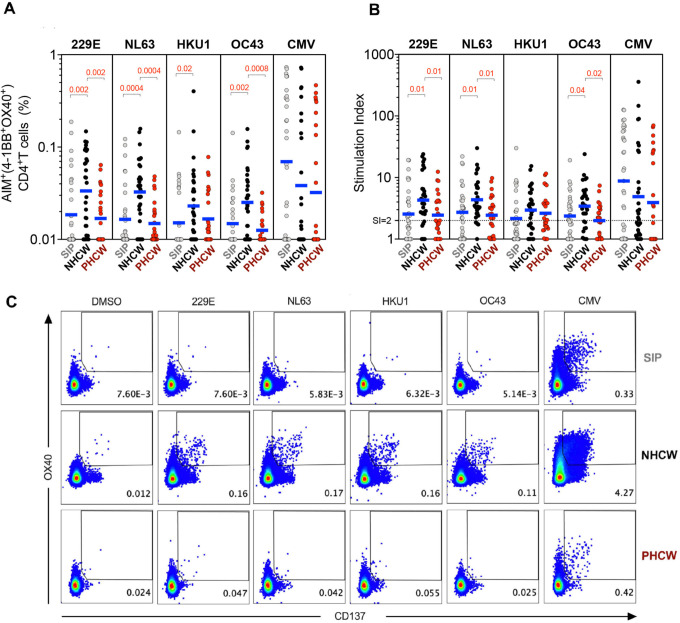
Figure 2. CD4+ T cell immune responses to CCC epitopes from Miami are higher in NHCW.
CCC-specific CD4+ T cells (HCoV-229E, HCoV-NL63, HCoV-HKU1 and HCoV-OC43) and ubiquitous control CMV-specific CD4+ T cells were measured as percentage of AIM+ (OX40+CD137+) CD4+ T cells after stimulation of PBMCs with CCC and CMV peptide pools. (A) Data background subtracted or (B) stimulation index (SI) against DMSO negative control are shown with geometric mean for the 3 different groups. Non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis multiple comparison test was applied for each individual CCC strain and CMV. P values are shown for the statistical significant comparisons. “SIP” = Shelter In Place community volunteers (n=33). “NHCW” = SeroNegative Health Care Workers (n=31). “PHCW” = Antibody or PCR Positive Health Care Workers (n=26). (C) Representative FACS plots, gated on total CD4+ T cells for the 4 CCC in addition to the DMSO and CMV across all the cohorts. Cell frequency for AIM+ cells in the several conditions is indicated.