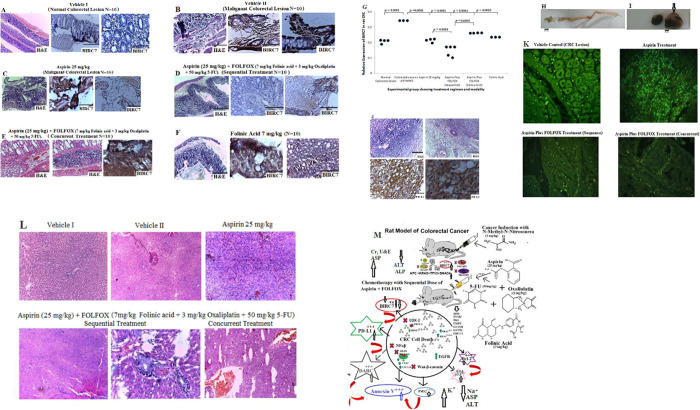
Fig 5. The treatment effect of aspirin with or without FOLFOX on apoptotic cell death in colorectal cancer in vivo in rat (scale bar = 50 μm for H&E and scale bar = 100 μm for IHC).
A—F show various pattern of BIRC7/Livin expression in aspirin with or without FOLFOX treated rats and also in untreated group. G shows relative expression of the BIRC7 in rats typified in dot plot. H CRC-bearing rats treated with oxaliplatin showing obstructed colonic lumen devoid of faecal material. I show an enlarged abnormal Kidney (arrowed) from the oxaliplatin-treated rat observed during the post mortem. J Sections of enlarged kidney showing features of renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation with positive expression of PD-L1. K Sections showing different IF staining pattern upon treatment with aspirin only and aspirin plus FOLFOX in sequence and concurrent. L Sections of the liver showing preserved architecture that is devoid of haemorrhage in the group of rats treated with aspirin plus FOLFOX in sequence compared with concurrent treatment. M describes the possible pathways of the effect of sequential treatment of aspirin plus FOLFOX during tumour induction and chemotherapy. Several pathways are responsible for the aspirin and FOLFOX drug metabolism, transport and target mechanisms and they include but not limited to: COX2 inhibition, NFkB and Wnt-B-Catenin signalling pathways for aspirin; dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), thymidine phosphorylase (TYMP), thymidine kinase 1 (TK1) and uridine monophosphate synthetase (UMPS) for fluoropyrimidine component, 5-FU; and excision cross-complementing genes (ERCC) and glutathione S-transferases (GSTM) for the oxaliplatin (trans-1-diaminocyclohexane oxalateplatinum). These non-exhaustive have significant role in BIRC7, DARC, Annexin V, PD-L1, PMS2, EGFR, BRAF, KRAS, MDSC, PIK3CA, p53, BCL2 expression and functions. In NMU-induced colon carcinogenesis in rats, there is marked destruction of lymphocytes and granulocytes, significant reduction of red blood cells, platelet and total white blood cells. This was followed by reduction in alanine aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase levels with increase in creatinine, electrolytes, urea, and aspartate aminotransferase levels. Sequential treatment of aspirin plus FOLFOX may confer a better anti-tumour immune response in CRC and this is justified by increase expression of PD-L, DARC and suppression of BIRC7.