Figure 1:
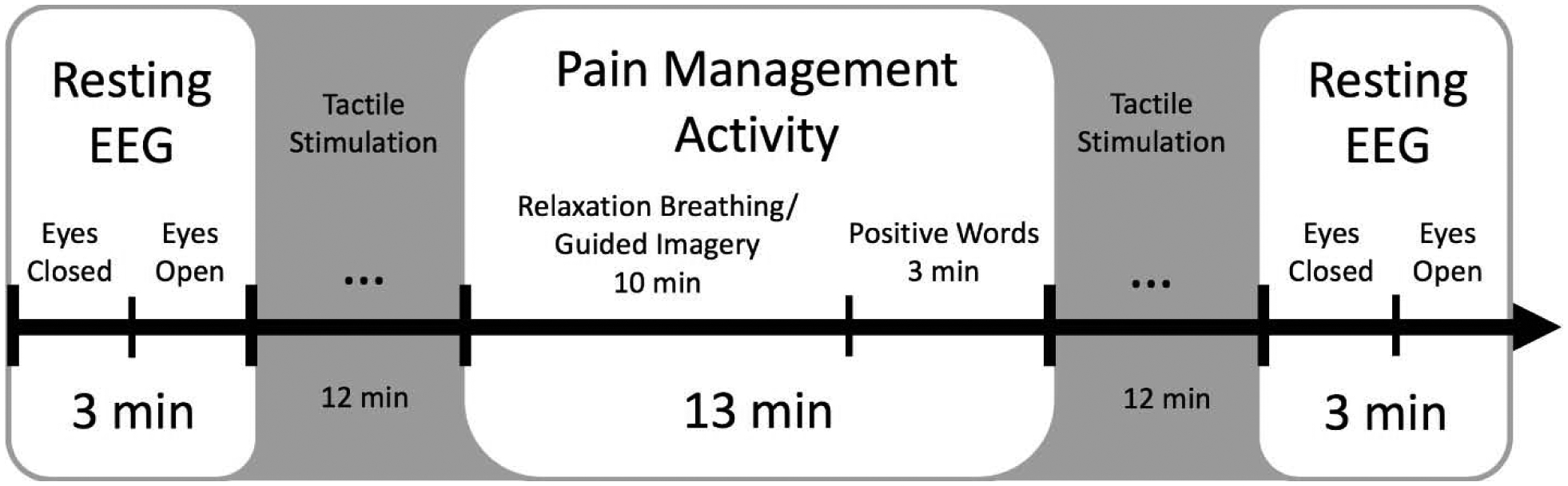
From left to right, each of two experimental sessions started with the recording of a 3-minute electroencephalography (EEG) resting block, followed by a somatosensory stimulation block, a period of relaxation breathing/guided imagery/positive affect activity, another tactile stimulation block, and a final resting block. The resting blocks comprised an initial 90-second eyes-closed condition, followed by 90-second eyes-open condition. Each block from which alpha measures were taken is presented in white. These blocks were used as items for calculating Cronbach’s α and Pearson’s correlation coefficients. Somatosensory stimulation blocks included a 3-minute stimulation for each of four sites: the left wrist, right wrist, left knee, and right knee.
