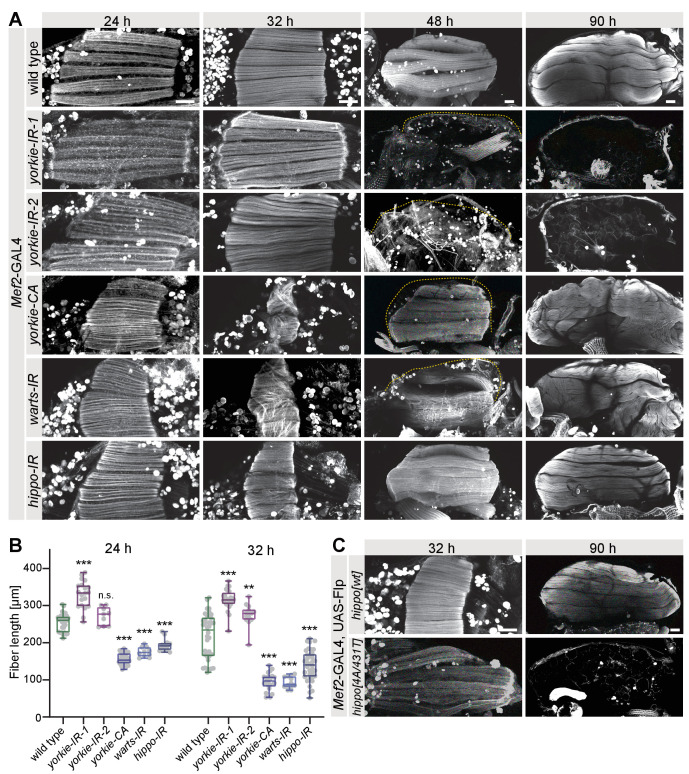
Figure 4. The Hippo pathway regulates muscle morphogenesis.
(A) Flight muscles at 24 hr, 32 hr, 48 hr, and 90 hr after puparium formation (APF) from wild type, yorkie knock-down (independent RNAi lines IR-1 and 2), yorkie-CA, as well as warts and hippo knockdown genotypes stained for actin. The dotted lines highlight the cuticle. Note the too long yorkie-IR muscles but too short yorkie-CA, warts-IR, and hippo-IR muscles at 24 hr and 32 hr APF. (B) Box plot showing muscle fiber length at 24 hr and 32 hr APF of the indicated genotypes. Student’s t-test, *** p-value<0.001, **p value<0.01. (C) Flight muscles at 32 hr and 90 hr APF from pupae expressing either wild-type hippo or Slmap-binding-deficient hippo[4A/431T] (under control of the milder tubulin promoter). The FRT stop cassette is removed by muscle-specific Mef2-GAL4-driven Flp recombinase. All scale bars represent 50 µm.