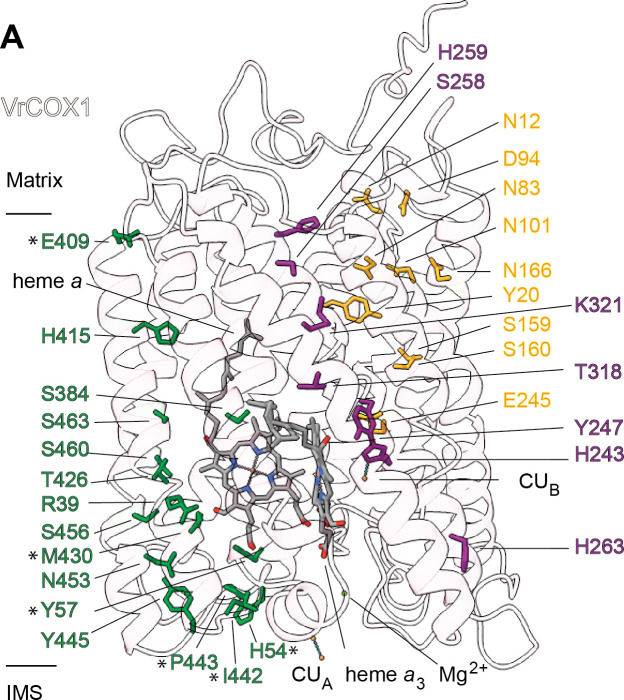
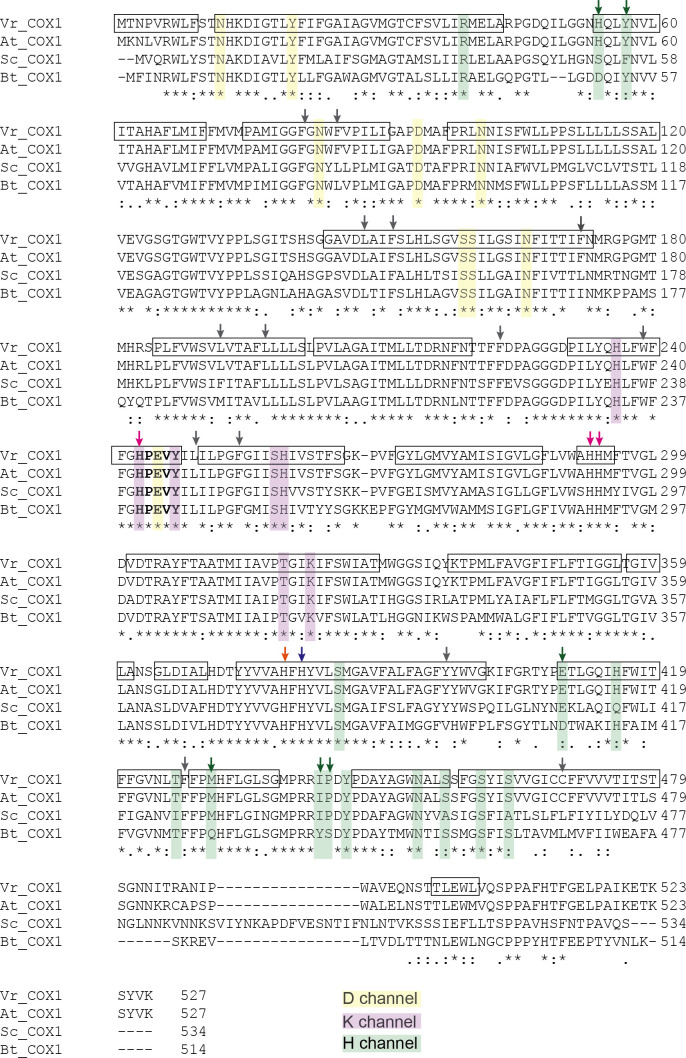
COX1 sequences from
V. radiata (Vr),
Arabidopsis thaliana (At),
S. cerevisiae (Sc), and
B. taurus (Bt) were aligned with Clustal Omega. Proton pathway residues are highlighted: D channel in yellow, H channel in green and K channel in purple. Proton-channel residues that differ between
V. radiata and
B. taurus are marked with an arrow of the same color as the channel to which the residue belongs. Boxes indicate α-helices in the VrCOX1 atomic model. Key residues are marked with arrows: heme
a-coordinating residues in blue, heme
a3-coordinating residues in orange, CU
B-coordinating residues in magenta. RNA-editing sites are marked with gray arrows, see also
Supplementary file 1d. The HPEVY ring is bolded. Symbols underneath aligned residues: * fully conserved, : conservation between group of strongly similar properties, . conservation between group of weakly similar properties.