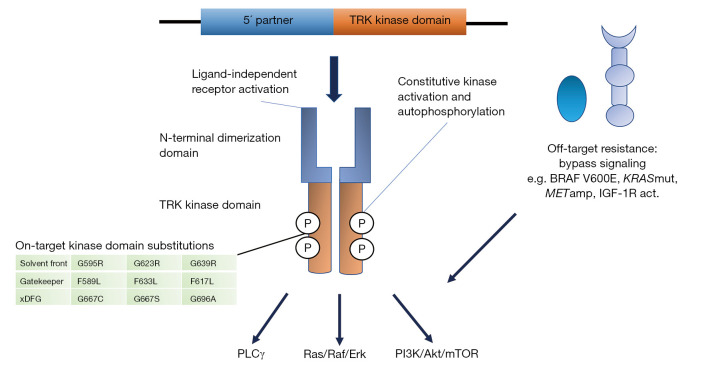
Figure 1.
Constitutive activation of the TRK receptors occurs through different chromosomal rearrangements resulting in in-frame fusions of the C-terminal tyrosine kinase domain of the NTRK genes with an N-terminal fusion partner. The fusion results in ligand-independent dimerisation and autophosphorylation of the receptors, leading to constitutive activation of downstream signaling pathways, including Ras/Raf/Erk, PI3K/Akt/mTOR and PLCγ pathways. Acquired resistance to TRK inhibitors are mediated by either on-target substitutions in the kinase domain (in solvent front, gatekeeper region or xDFG motif) or off-target activation of bypass signaling pathways. KRASmut, KRAS mutation; METamp, MET amplification; IGF-1R act, IGF-1R activation.