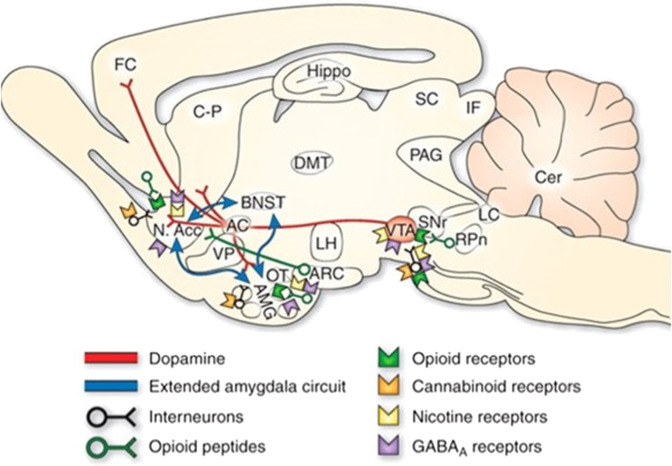
Fig. 2. Rat brain neurochemical neurocircuits in drug reward (From [101]).
Sagittal section through a representative rodent brain illustrating the pathways and receptor systems implicated in the acute reinforcing actions of drugs of abuse. Cocaine and amphetamines activate the release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens and amygdala through direct actions on dopamine terminals. Opioids activate opioid receptors in the VTA, nucleus accumbens, and amygdala through direct or indirect actions via interneurons. Opioids facilitate the release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens by an action either in the VTA or the nucleus accumbens, but also are hypothesized to activate elements independent of the dopamine system. Alcohol activates g-aminobutyric acid-A (GABAA) receptors or GABA release in the VTA, nucleus accumbens, and amygdala by either direct actions at the GABAA receptor or through indirect release of GABA. Alcohol is hypothesized to facilitate the release of opioid peptides in the VTA, nucleus accumbens, and central nucleus of the amygdala. Alcohol facilitates the release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens through an action either in the VTA or the nucleus accumbens. Nicotine activates nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the VTA, nucleus accumbens, and amygdala, either directly or indirectly, through actions on interneurons. Cannabinoids activate cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the VTA, nucleus accumbens, and amygdala. Cannabinoids facilitate the release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens through an unknown mechanism either in the VTA or the nucleus accumbens. The blue arrows represent the interactions within the extended amygdala system hypothesized to have a key function in drug reinforcement. The medial forebrain bundle represents ascending and descending projections between the ventral forebrain (nucleus accumbens, olfactory tubercle, septal area) and the ventral midbrain (VTA) (not shown in figure for clarity). AC anterior commissure, AMG amygdala, ARC arcuate nucleus, BNST bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, Cer cerebellum, C-P caudate-putamen, DMT dorsomedial thalamus, FC frontal cortex, Hippo hippocampus, IF inferior colliculus, LC locus coeruleus, LH lateral hypothalamus, N Acc. nucleus accumbens, OT olfactory tract, PAG periaqueductal gray, RPn reticular pontine nucleus, SC superior colliculus, SNr substantia nigra pars reticulata, VP ventral pallidum, VTA ventral tegmental area.