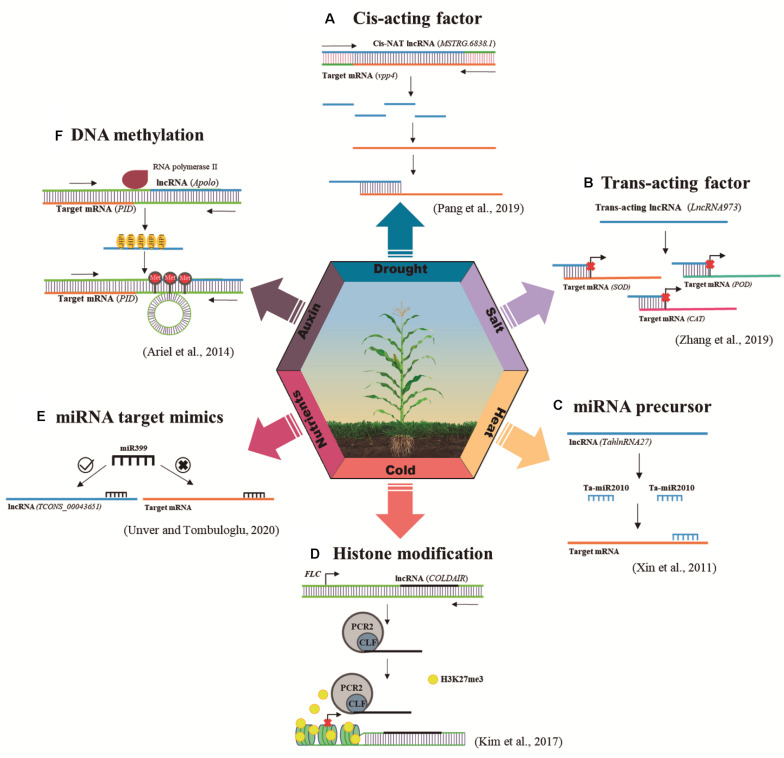
FIGURE 1.
Regulatory mechanisms of plant lncRNAs in response to abiotic stresses. The main mechanisms of action triggered by lncRNAs responsive to abiotic stresses are miRNA precursor, histone modification, target mimicry, RdDM, cis-acting factor and trans-acting factor. This figure illustrates one example of each of these mechanisms. (A) Cis-acting factor: vpp4 encoding a vacuolar (H+)-pumping ATPase subunit was identified as a putative target of an adjacent lncRNA MSTRG.6838.1. The expressions of vpp4 and MSTRG.6838.1 were significantly correlated in many tissues and development stages, being both repressed under drought stress, which indicates that MSTRG.6838.1 and vpp4 could be a promising cis-acting pair (Pang et al., 2019). (B) Trans-acting factor: LncRNA973 corresponds to a trans-acting lncRNA responsive to salt stress, which regulates plant stress responses by modulating the expression of a series of key salt-related genes, as superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), and catalase (CAT) (Zhang et al., 2019). (C) miRNA precursor: TahlnRNA27, a heat-induced lncRNA, can act as a miRNA precursor since it presents Ta-miR2010 family sequences. After 1 h of heat-treatment, TahlnRNA27 expression was induced as well as Ta-miR2010 expression. The secondary structure and the corresponding expression pattern indicate that TahlnRNA27 might be the precursor of Ta-miR2010 (Xin et al., 2011). (D) Histone modification: The repression of FLC by vernalization is accompanied by a series of changes in histone modifications at FLC chromatin, including the deposition of repressive histone markers, such as Histone H3 Lys 27 (H3K27me3). COLDAIR is up-regulated in response to cold, physically interacting with a component of PRC2, CURLY LEAF (CLF), for the increased enrichment of PRC2 at FLC chromatin to promote H3K27me3 accumulation at FLC (Kim et al., 2017). (E) miRNA target mimics: TCONS_00043651 function as a potential natural miRNA sponge of miR399 sequence in response to boron-stress. Results obtained from barley roots analysis showed that TCONS_00043651 was up-regulated (three times than that of control) upon boron-exposure, meanwhile miR399 expression was repressed (three times down-regulated) in the same stress conditions (Unver and Tombuloglu, 2020). (F) DNA methylation: APOLO can trigger RdDM in response to an auxin stimulus. In response to auxin, Pol II APOLO transcripts gradually recruit LHP1 to mediate loop formation, whereas Pol IV/V transcription triggers DNA methylation. Then, Pol II APOLO-LHP1 mediated loop is conformed and maintained by Pol IV/V-dependent DNA methylation to repress PID expression (Ariel et al., 2014).