Figure 1.
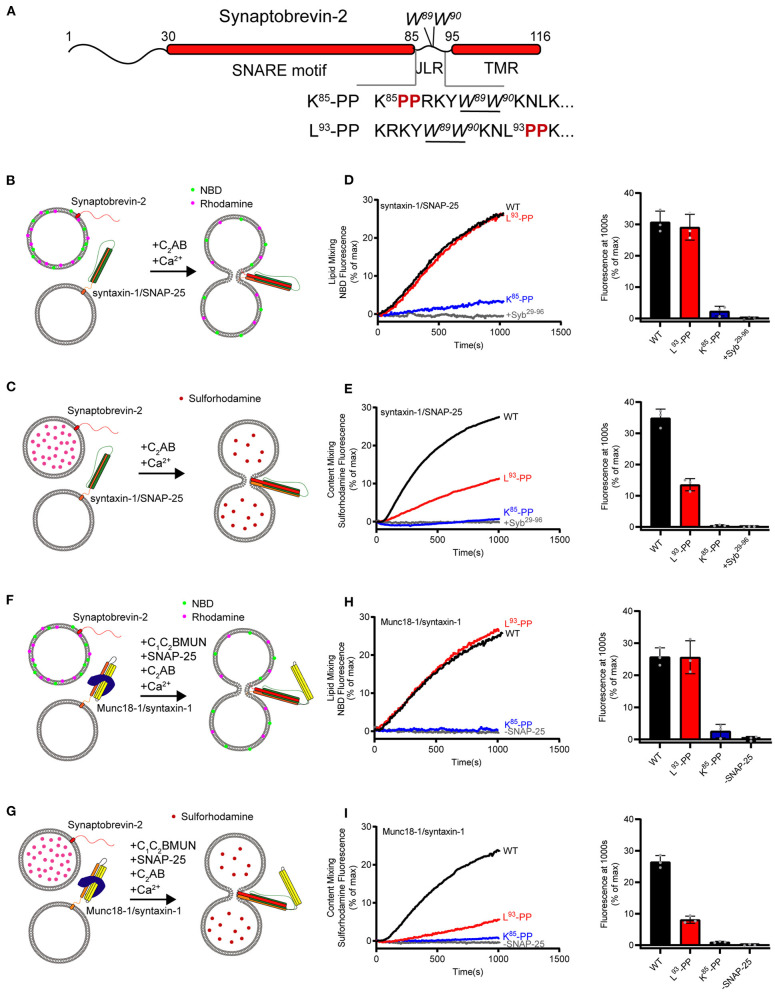
Fusion affected by disrupting helical continuity of the synaptobrevin-2. (A) Domain structure of full length wild-type synaptobrevin-2 (WT) and its mutants with two-proline insertions after K85 (K85-PP) or L93 (L93-PP) in the JLR. (B,C) Scheme of lipid mixing (B) and content mixing assay (C) between syntaxin-1/SNAP-25 and synaptobrevin-2 liposomes in the presence of C2AB fragment and 1 mM Ca2+. Note that the syntaxin-1 SNARE motif (H3, residues 183–288) was used here to form the syntaxin-1/SNAP-25 complex. (D,E) Lipid (D) and content mixing (E) of synaptobrevin-2 WT, K85-PP, and L93-PP liposomes with syntaxin-1/SNAP-25 liposomes. (F,G) Scheme of lipid mixing (F) and content mixing assay (G) between Munc18-1/syntaxin-1 (full length, residues 1–288) and synaptobrevin-2 liposomes in the presence of the Munc13-1 C1-C2B-MUN fragment, SNAP-25, C2AB fragment, and 1 mM Ca2+. (H,I) Lipid (H) and content mixing (I) of synaptobrevin-2 WT, K85-PP, and L93-PP liposomes with Munc18-1/syntaxin-1 liposomes. Representative traces came from one of three independent experiments. Bars on the right panel in (D,E,H,I) are means ± SDs, n = 3.