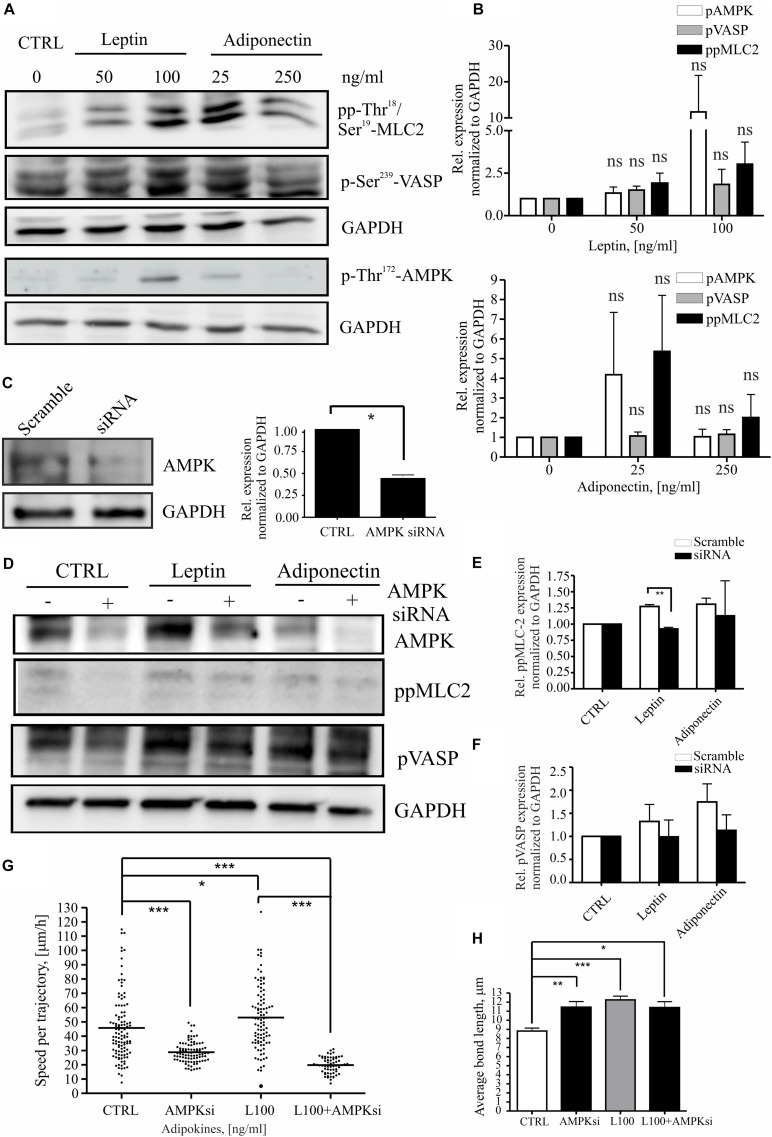
FIGURE 3.
Leptin induces MLC-2 phosphorylation. (A) Western blot analysis of cellular lysates from MCF10A cells. Specific antibodies against pp-Thr18/Ser19-MLC2, p-Thr172-AMPK and p-Ser239 VASP were utilized. GAPDH acts as a loading control. (B) Quantifications of the Western blots, related to (A). n = 3, Student’s t-test, NS (not significant). (C) Representative Western blot of ctrl siRNA and AMPK siRNA-treated MCF10A cells. Specific antibodies against AMPK and GAPDH were utilized. Quantification of the siRNA experiments, n = 3, *p < 0.05, Student’s t-test. (D) AMPK interference significantly affects MLC-2 phosphorylation. Western blot analysis of cellular lysates from MCF10A cells, left untreated or treated with either leptin or adiponectin and siRNA against AMPK. Specific antibodies against p-Ser239-VASP, pp-Thr18/Ser19-MLC-2, total VASP or AMPK were utilized. GAPDH acts as a loading control. (E) Quantifications of the Western blots, related to (D) pp-MLC-2 and (F) pVASP; mean values ± SEM, n = 3; **p < 0.01, Student’s t-test. (G) median values of cell speed per trajectory of leptin 100 ng/ml with or without AMPK siRNA, results are from at least 62 cells per condition. n = 2, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, One-way ANOVA, Bonferroni’s post-test. (H) the cell-to-cell bond length calculated similarly to Figure 2B, but in cells treated with leptin 100 ng/ml with or without AMPK siRNA, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post-test.