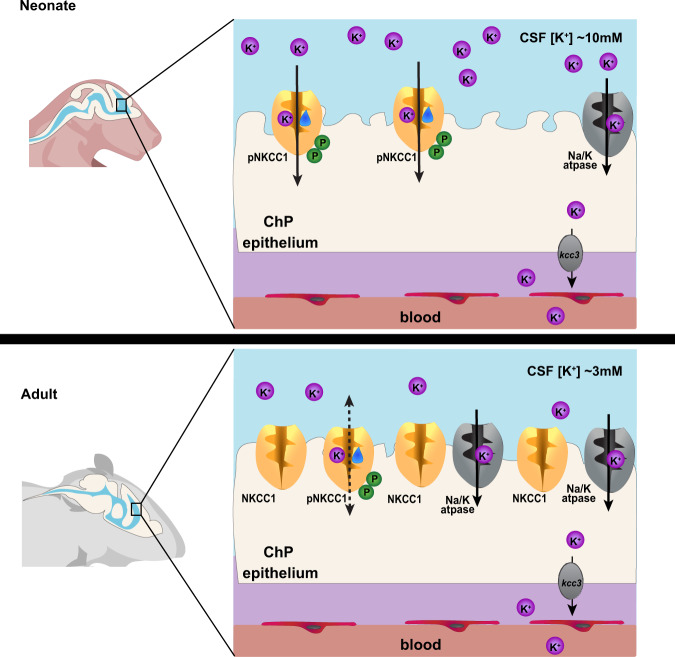
Fig. 7. Working model of ChP NKCC1 mediating K+-driven CSF outflow.
The schematics depict ChP NKCC1-mediated K+ and water clearance from CSF in neonatal mice, in comparison to the adult scenario. For simplicity and clarity, only K+ is depicted among all ions and only NKCC1 and Na+/K+-ATPase are included. Neonatal (P0-7, above) ChP has higher pNKCC1 expression than adult ChP, albeit lower total NKCC1. Neonatal CSF [K+] is 2–3 fold higher than adult. With similar [Na+] and [Cl−], this [K+] difference is sufficient to alter the total Nernst potential of epithelial cells and bias NKCC1 transport of K+, together with water, out of CSF and into the ChP in neonates.