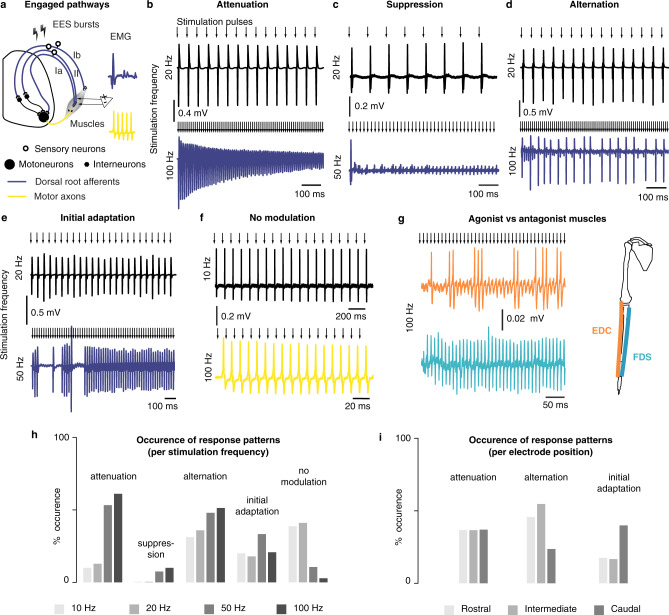
Fig. 7. Patterns of muscular responses elicited during high-frequency stimulation of the cervical spinal cord of monkeys.
a Diagram of the presumed engaged pathways during high-frequency stimulation when muscular responses are modulated and unmodulated, respectively. b–e Examples of frequency-dependent modulation of muscular responses. In each panel, the top and bottom EMG traces were recorded in the same muscle and using the same stimulation amplitude (near motor threshold) but different frequencies. f Example of absence of frequency-dependent modulation. g Example of absence of correlation of frequency-dependent modulation between antagonist muscles (the top and bottom traces are simultaneous recordings of the extensor digitorum communis (EDC) and flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) muscles of Mk-Lo during the same stimulation pulse train). h Frequency of occurrence of modulation patterns with respect to stimulation frequency. All the patterns recorded in all the muscles of the 4 animals in which high-frequency stimulation was tested were included in the analysis (n = 80 patterns at 10 Hz, n = 39 patterns at 20 Hz, n = 75 patterns at 50 Hz, n = 72 patterns at 100 Hz). i Same as (h), but with respect to electrode position (n = 132 patterns for rostral electrodes, n = 66 patterns for intermediate electrodes, and n = 68 patterns for caudal electrodes).