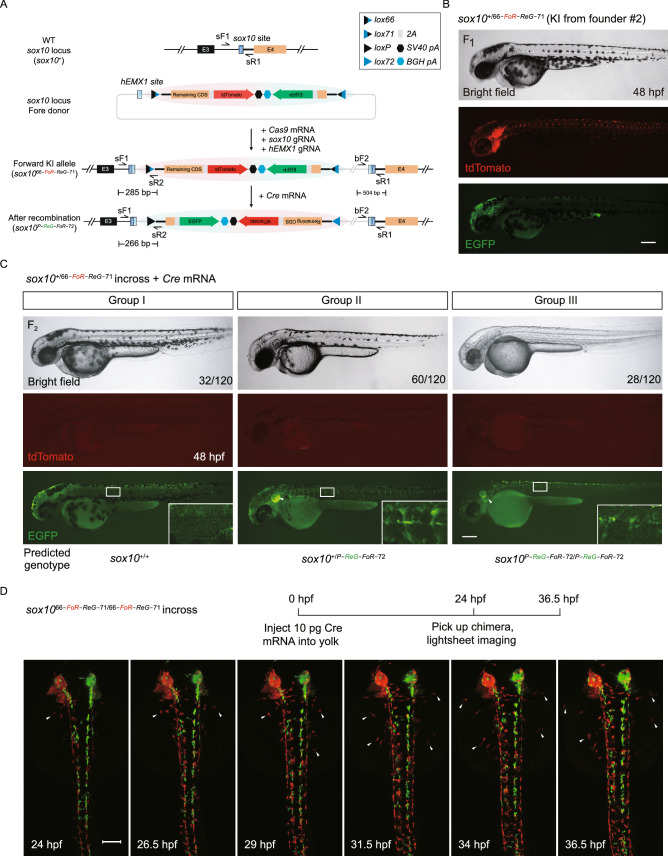
Figure 1.
Generation and evaluation of fluorescent reporter-tagged conditional knockout alleles at the zebrafish sox10 locus and mosaic tracing analysis of sox10 expressing cells. (A) Schematic diagram of the KI strategy of sox10 FoRe donor consisting of two components in opposite orientations (highlighted by red shadow for the Forward component for maintaining the function of sox10, and green shadow for the Reverse component for disrupting the function of sox10). The sox10 CRISPR/Cas target site is shown as a dark blue box, and the hEMX1 target site is shown as a light blue box. (B) Images of a 48 hpf F1 embryo from germline transmission screening of the sox10 FoRe donor KI founder. Scale bar, 200 μm. (C) Phenotype analysis of the 48 hpf F2 embryos from the incross of sox10+/66-PoR-ReG−71 heterozygotes (derived from F0 #2) after the injection of 50 pg Cre mRNA at the one-cell stage. The white arrowheads indicate otic vesicles. Detailed sox10 expression in the trunk region can be seen under higher magnification of the boxed areas. Scale bar, 200 μm. (D) Serial lightsheet images of a sox10 mosaic embryo from incross of sox1066-FoR-ReG−71/66-FoR-ReG−71 homozygotes after vegetal pole injection of 10 pg Cre mRNA and recorded from 24 hpf to 36.5 hpf. Some of the tdTomato-positive neural crest cells could migrate to the two sides of the body (as indicated by the white arrowheads), while all of the EGFP-positive cells remained in the middle. Scale bar, 100 μm