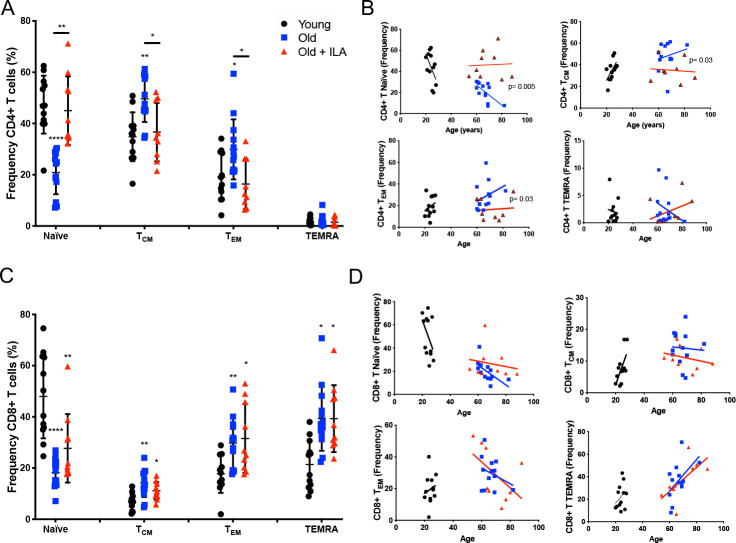
Figure 2.
Frequency of naïve and memory CD4+T cells are altered in persons with interstitial lung abnormalities (ILA) compared with old control group. Peripheral mononuclear cells were prepared to flow cytometry. First, live cells were identified, and the gate of CD3+CD4+ or CD3+CD8+T cells was delimited. Then, CCR7 and CD45RA expression were evaluated to obtain the frequency of: Naïve (CD45RA+CCR7+), central Memory (CM, CD45RA-CCR7+), effector Memory (EM, CD45RA-CCR7-) and TEMRA (CD45RA+CCR7-) in CD4+ or CD8+T cells subpopulations (panel A and C, respectively). Panel B: Individual variations in their rate of change of CD4+T cells subpopulations over age; graphic shows the individual-behaviour of each individual, and the regression line per group-age (line colour per group is indicated). Panel D: Individuals vary in their rate of change of CD8+T cells subpopulations over age; graphic shows the individual-behaviour of each individual and the regression line per group-age (line colour per group is indicated). Graphs show individual values, mean±SD (young: n=12, old: n=13, old+ILA: n=10). *p<0.05 **p<0.01 ***p<0.0001. Statistical analysis was performed with multiple t-tests and a Holm-Sidak method was used to adjustment for multiple comparisons; asterisks indicate comparison of the three groups. When the asterisk is on a line, indicates, the comparison between old control group and old +ILA. CCR7, C-C chemokine receptor 7; TCM, central memory; TEM, effector memory; TEMRA, effector memory RA.