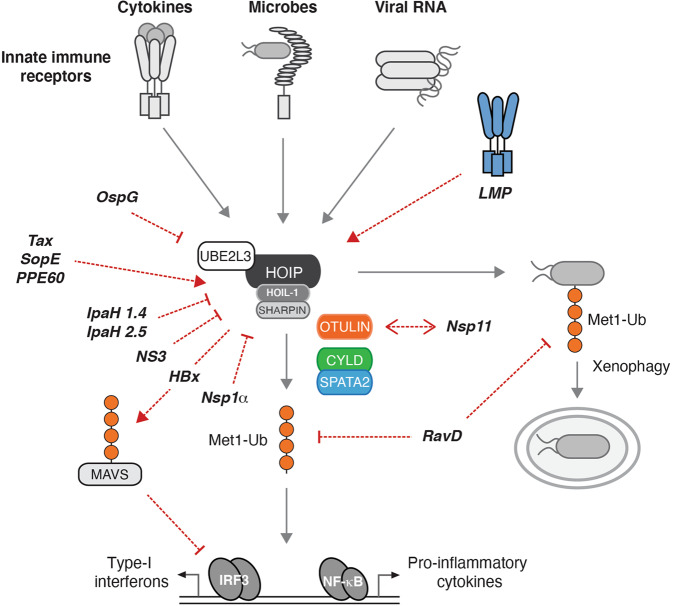
Fig. 4. Pathogen effectors targeting the Met1-Ub machinery.
Schematic model of the major Met1-Ub-controlled pathways activated by pathogens, and of the bacterial and viral effectors that modulate the Met1-Ub machinery. Activation of receptors by cytokines or molecular patterns from microbes leads to the formation of Met1-Ub and ultimately transmission of signals from the activated receptor to initiate anti-bacterial autophagy or transcription factor activation via nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and interferon response factor 3 (IRF3). Red arrows and lines denote where in the pathway the effectors exert their function. The pathogen effectors depicted target Met1-Ub in various direct or indirect ways. Abbreviations: HBx hepatitis B virus X protein, IpaH1.4 invasion plasmid antigen H1.4, IpaH2.5 invasion plasmid antigen H2.5, IRF7 interferon regulatory factor 7, LMP1 latent membrane protein 1, MAVS mitochondrial antiviral-signalling protein, NS3 non-structural protein 3, NSP1α non-structural protein 1α, Nsp11 non-structural protein 11, OspG outer Shigella protein G, PPE60 proline–proline–glutamate motifs 60, RavD region allowing vacuole colocalization D, SopE Salmonella outer protein E, Tax trans-activator protein X.