Figure 1.
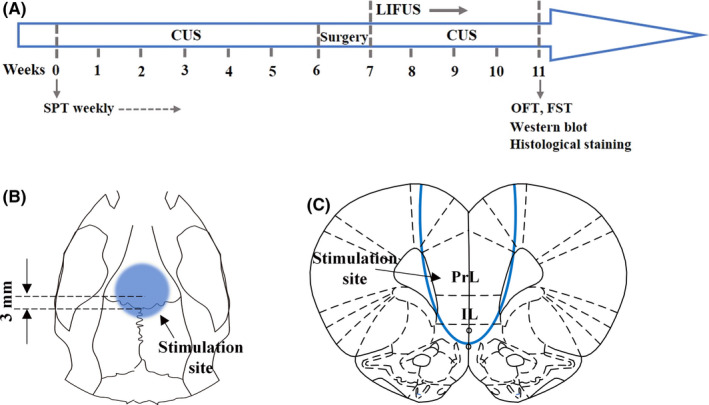
Overview of the experimental procedures. A, The timeline of the experiments. After 1 week of adaptation, the control group were fed normally in pairs. Rats in the CUS group were housed in individual cages and subjected to one or two of fourteen randomly selected different stressors per day for six consecutive weeks. After completion of the CUS exposure, each rat was fixed with an ultrasound collimator on the skull and was allowed 1 week to recover from surgery. Normal control rats had holes drilled into the skull, but the collimator was not affixed. Then, ultrasound stimulation was applied to awake and freely moving rats in the CUS + LIPUS group, for twenty minutes each day for four consecutive weeks. Rats in the control and CUS + sham LIPUS groups underwent the same procedures, but the power was turned off. Behavioral tests were conducted immediately after LIPUS. After that, rats were sacrificed, and their brains were removed for morphological and biochemical experiments. (B, C) Anatomical schematic of the stimulation area. A custom‐designed acoustic collimator was fixed on the skull covering the vmPFC (The center of the circle is anteroposterior + 3.0 mm; medial‐lateral 0 mm)
