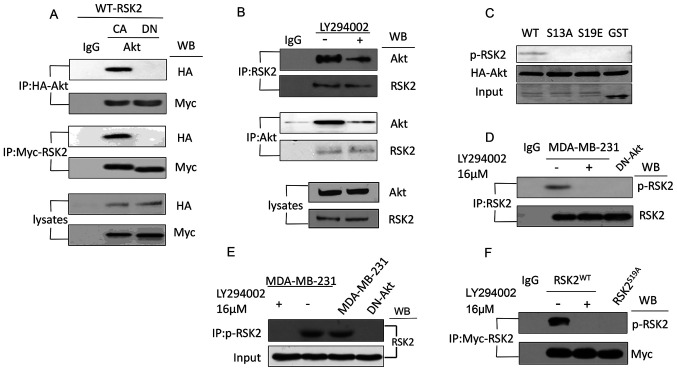
Figure 2.
Akt interacts with and phosphorylates RSK2 at S19. (A) Co-IP was used to analyze the lysates from the MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with the CA-Akt and DN-Akt plasmids using antibodies targeting HA and Myc. (B) Co-IP was used to detect the interaction of endogenous RSK2 and Akt in the MDA-MB-231 cells with or without the PI3K-Akt inhibitor LY294002. (C) A western blot was used to observe the phosphorylation of RSK2 in the MDA-MB-231 cells with WT- or mutant-RSK2 at the S19 site. (D) Endogenous RSK2 was immunoprecipitated using a RSK2-antibody or a p-RSK2 antibody in the MDA-MB-231 cells treated with or without LY294002 or the MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with DN-Akt. (E) The antibody targeting p-RSK2 was used to immunoprecipitate the phosphorylated endogenous RSK2, and the antibody targeting RSK2 was used for the western blotting assay. (F) An IP was performed to assess RSK2 in the cells transfected with the WT-RSK2 (in the presence or absence of LY294002) or RSK2S19A plasmids, and the precipitates were subjected to a western blot using the antibody targeting p-RSK2. S19, Ser19; WB, western blotting; RSK2, ribosomal S6 kinase 2; RSK2S19A, RSK2 Ser19Ala; CA, constitutively activated; DN, dominant negative; p-, phosphorylated; HA, hemagglutinin; IP, immunoprecipitation; IgG, immunoglobulin G.