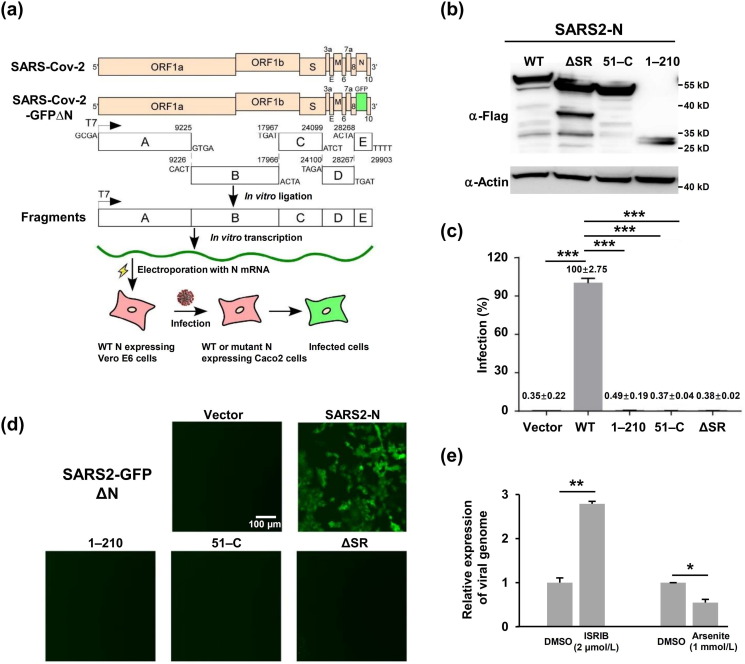
Fig. 5.
The SARS-CoV-2 N protein-based genetic complementation system is utilized to assess WT or mutant N protein function in the viral life cycle. (a) Schematic diagram illuminating the SARS-CoV-2 N protein-based genetic complementation system for the assessment of N or N mutant function in the viral life cycle. (b) Immunoblotting assays were performed to detect the expression of different versions of the N proteins in Caco-2 cells transduced by lentivirus. (c) Flow cytometry quantified the percentage of GFP positive cells. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed with unpaired t-test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). (d) Live-cell fluorescence microscopy of Caco-2-N cells infected by the cell culture supernatant from Caco-2 cells expressing different versions of the N protein. (e) SG assembly regulated SARS-CoV-2 infection. Caco-2 cells were pretreated with 1 mmol/L arsenite for 1 h prior to SARS-CoV-2 GFP ΔN virus infection at an MOI of 0.05. Caco-2 cells were treated with 2 μmol/L ISRIB and infected with SARS-CoV-2 GFP ΔN virus at MOI of 0.05. Viral genomic RNA expression was normalized to that of the DMSO treated control. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed with unpaired t-test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).